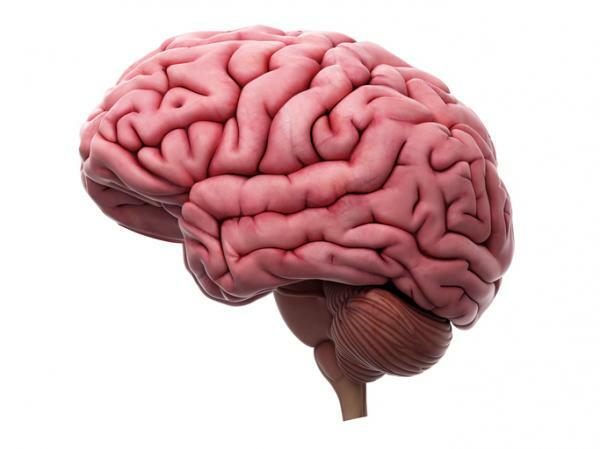
The human being resembles a machine whose complex operation is controlled by the Central Nervous System (CNS), which would be equivalent to the internal processor of a computer. Within the CNS, the brain is one of its parts and is responsible for the control of the most complex brain functions and for managing and coordinating with other systems.
In this Psychology-Online article we will see how the human brain works. We will explain in a little more detail what the brain is and within which system it is included, we will describe its anatomy and we will detail its parts with their respective functions. Finally, we will share ten important tips to keep your brain healthy and active.
Index
- What is the brain and what system does it belong to
- Human brain anatomy: areas
- Parts of the brain and their functions
- How the human brain works
- Keys to proper brain function
What is the brain and what system does it belong to.
The brain is the largest part of the brain
The cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem are part of the brain, located in the skull that, together with the spinal cord, make up the Central Nervous System. The brain belongs to the nervous system.
Anatomy of the human brain: areas.
The human brain It is made up of two parts: the cerebral cortex and the diencephalon.
The cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a rough area divided by furrows, one of which divides the brain into two hemispheres, the right and the left. In these two hemispheres, there are several regions called lobes that fulfill very specific functions. Specifically, there are four lobes whose names are due to the bone with which they contact: frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe and temporal lobe. In the next section we will explain in detail its functions.
The diencephalon
It is housedor at the base of the skull and is made up of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary
- Thalamus: center for processing sensitive and motor information and intervenes at the level of attention and alertness. The thalamus sends the sensations to the cerebral cortex to make them conscious
- Hypothalamus and pituitary: they are part of the endocrine system and regulate many functions of our body through the production of hormones and other mechanisms related to emotions (sweating, dilated pupils, tearing, heart rate), regulation of body temperature, appetite and satiety, sleep and wakefulness and appetite sexual. Here you will find more information about the pituitary gland, also called pituitary gland.
Parts of the brain and their functions.
In this section we will specify the functions that each of the four lobes of the cerebral cortex:
- Frontal lobe: It is located in the anterior part of the cerebral cortex and is responsible for managing voluntary motor behavior. It is a highly developed area in the human being that, simultaneously, houses the most cognitive functions. complex such as reasoning, problem solving, language articulation, and control emotional.
- Parietal lobe: also called the somatosensory cortex, we find it in the posterior, middle and lateral part of the brain and is responsible for the processing of sensations and perceptions, touch, pressure, temperature and pain. It is responsible for the integration of interoceptive information (from inside our body: muscles, joints and tendons) with the external one (information from outside).
- Occipital lobe: It is the smallest region and is located in the posterior and lower part of the cerebral cortex, below the parietal lobe. Its most prominent functions are image processing, vision, spatial recognition and discrimination of movement and colors.
- Temporal lobe: It is located in front of the occipital lobe on the inside, between the temples. This brain area is responsible for smell, hearing, balance, and coordination. It is related to the limbic system, so it plays an important role in the experience of the basic emotions (joy, fear, anger and sadness).
How the human brain works.
The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron. Its function is to receive messages from other cells, decide whether or not to send the information and do it efficiently. exist sensory neurons, that receive information from the sensory systems and take it to the CNS; motor neurons, which transmit motor activation information from the brain to the muscles and calls interneurons, which transmit information locally, within the SNC. In the following article you will find more information about types of neurons and their functions.
They are made up of four parts: the body, the axon, the dendrites, and the synapses. The dendrites of the neuron receive the neurotransmitter substance from another neuron and activate the neuron, the information is processed and the final information is sent through the output circuit, the axon. This will be in charge of activating, through neurotransmitter substances, the dendrites of other neurons. And so it happens successively. The synapse will be the moment of chemical excitation that joins two neurons.
The synapse produced between two neurons leaves them sensitive, over a period of hours or days, to an easier activation if they are stimulated again. It will be necessary to repeatedly activate the different networks between neurons to form complex neural patterns that shape thoughts, emotions, and perceptions. That is why, although the anatomical architecture of the brain is common to the entire species, neural networks will vary from one person to another depending on the particular stimulation that each one of us makes of the different associations synaptic. This is called brain plasticity, a function that characterizes the human brain.
Keys to the proper functioning of the brain.
Actually, to maintain a healthy brain we only have to maintain Healthy habits. These habits are necessary to maintain our general health (physical, psychological and emotional). If we take into account that the brain is the center from where most of the functions and systems are controlled humans, it is logical to understand that to keep the brain healthy we must incorporate healthy habits into our lifetime.
Specifically, we can talk about 10 essential habits or routines to keep our brain young and healthy:
- Do activities that keep us mentally active
- Perform moderate physical exercise
- Maintain healthy social relationships
- Follow a healthy diet
- Reduce or eliminate the use of tobacco, alcohol, or other drugs
- Get 6 to 8 hours of restful sleep
- Control blood pressure (hypertension is a risk factor for brain problems)
- Prevent risk situations that may increase the chances of accidents and blows to the head
- Avoid diabetes and hypoglycemia (they are risk factors for brain problems)
- Keep a positive attitude before life and personal care
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to How the human brain works, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Dahl, W. J., & Barad, A. (2018). Diet and Brain Health. EDIS, 2018(2).
- Pasqual Maragall Foundation. 8 tips to maintain a healthy brain. Recovered from: https://blog.fpmaragall.org/cerebro-sano
- Geffner, D. (2014). The brain organization and function.


