The limbic system is that part of our brain in charge of regulating the physiological and emotional responses of our body. The anatomical structures of the limbic system are responsible for processing our emotions and regulating our behavior. This part of the brain has always aroused a lot of curiosity in the scientific community and in the world of psychology, that is because It is incredible to investigate how such a specific part of our anatomy can regulate something as important as our emotions.
In Psychology-Online, we will try to list the functions of this system and describe its anatomy with images that accurately illustrate the information provided. If you are interested in the limbic system, its parts, functions and diseases, we invite you to continue reading the following article.
Index
- What is the limbic system
- Limbic System Anatomy: Main Parts
- Limbic system: main functions
- Relationship between limbic system and emotions
- Limbic system: diseases
What is the limbic system.
This set of brain areas has not always been defined as we understand it today, throughout historical evolution and advances in neuroscience, the term "limbic system"It has evolved to the definition we have today.
Evolution of the term
Two centuries ago, a scientist named Paul Broca first referred to the limbic system to refer to the area adjacent to the Pineal gland. Broca spoke of a "great limbic lobe"and in that term he encompassed the entire medial aspect of the cerebral hemispheres around the corpus callosum. He also introduced olfactory bulbs into this large lobe (although these have little to do with emotion processing).
Later, James Papez discovered a circuit made up of nerve structures that are also part of the limbic system. This neurologist is known for being the first to propose a anatomical model for emotions and for putting under the scientific focus everything related to the sentimental plane.
We had to wait until 1952 for Paul MacLean to coin the term "limbic system" that we use today. This scientist defined the neural structures involved in that system and he proposed various theories about the brain and its evolution. In them, he affirmed that the emotional system was the most advanced of all of them (he defined it within the neo-mammalian brain) and that it was something properly of very advanced mammals.
Current definition of the limbic system
Today, we speak of the limbic system when we refer to the set of structures located in the brain (internal area of the brain) and whose main utility is the management and regulation of emotions. What we usually define as unconscious or irrational has its basis in a very specific area of the human anatomy. This system is made up of structures such as the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, the amygdala... among others that we will describe later.

Limbic system anatomy: main parts.
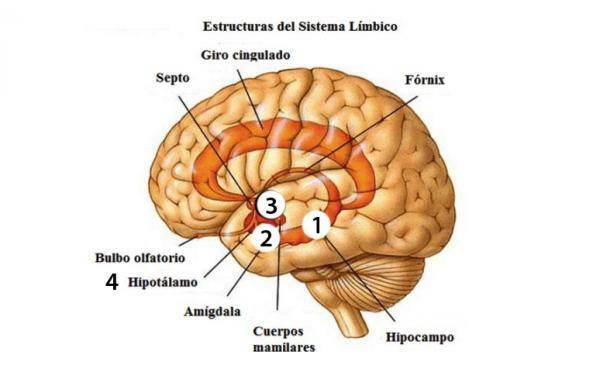
The limbic system or emotional nervous system it is located in the inner zone of our brain, beyond the cerebral cortex. It receives influences from many other pathways of the nervous system related to the senses: auditory, visual, olfactory systems, touch and taste sensors. Being interconnected with so many other pathways, it is very difficult to make a totally precise diagram of all its anatomical elements. Among the main parts of the system we highlight the following:
1. Hippocampus
This element is related to the transformation of recent memory to long-term memory and to autobiographical memory. We find it in the central part of the temporal lobe (1) and it also has an important function related to orientation and spatial memory.
2. Brain tonsil
The amygdala or tonsillar body is a mass of almond-shaped neurons located in the temporal lobes (2). This area of the limbic system is related to the formation and storage of memory associated with events or events that have produced strong emotions. The amygdala is said to be the seat of all emotions. In addition, recent studies also show that this element has a strong implication in the memory consolidation.
3. Thalamus
The thalamus is defined as the brain structure located above the hypothalamus (3). All sensory stimuli (except smell) pass through this area of our limbic system and then be derived to more specific areas. This part of our brain has the main function of behaving as a nucleus of connection and association of stimuli and emotional information.
4. Hypothalamus
This small element of our emotional nervous system (4) possesses is responsible for many neural functions. The hypothalamus is the most important area of the brain for managing and coordinating the balance of our body. This equilibrium is known as homeostasis and it is the process by which we regulate ourselves and can become stable in our environment. It has recently been discovered that it senses the levels of a protein called leptin when we eat too much and, in response to those levels, it decreases our appetite. It also regulates behaviors such as sleep cycles and the maintenance of body temperature.
5. Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia participate indirectly in the emotional nervous system, they are responsible for managing our motor responses (gestures or expressions) related to the emotional states produced by the other parts of the limbic system.
Parts of the limbic system
Next, we offer you a diagram so that you know better all the parts of this brain area
Limbic system: main functions.
As we have been repeating throughout this article, the limbic system is responsible for the regulation and motor expression of emotions. Here, we highlight the following functions of the limbic system:
- Seeks the self-preservation of the species by activating the homeostasis systems.
- It is responsible for managing most of the brain mechanisms to the memory.
- Circuits pleasure and addiction They pass through the amygdala, hippocampus, and other nuclei of the limbic system, so pleasant feelings begin right there.
- Activates the autonomic nervous system: it is responsible for sending signals to the nerves to maintain a alertness (sympathetic nervous system) or to inhibit alertness (nervous system parasympathetic).
- A possible involvement of the limbic system in some sexual behaviors.
The limbic system is the emotional brain?
When we talk about emotional experiences, a certain feeling of irrationality usually comes to mind, as if they were not part of our thinking mind. However, as we have shown, the brain is the main cause of our emotional responses. So we can affirm that our emotions are processed by the central nervous system.
Can we talk about emotional brain when we refer to the limbic system? Next, we will solve your doubts.
Relationship between limbic system and emotions.
As we have commented throughout this article, the limbic system has a large number of neural structures responsible for regulate emotions through neurotransmitters.
The limbic system regulates our body's responses to emotional stimuli. For example, it activates the alert systems and increases the heart rate when we are nervous or afraid. However, reducing its field of action to emotional responses is an approach that ignores many of the other functions that this system has and that we have mentioned previously.
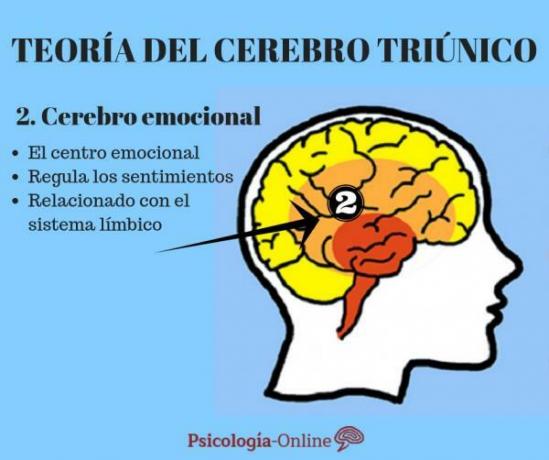
Thanks to the studies of James Papez or more recently McLean with his triune brain theory, the emotional cores in this brain system. In fact, the latter neurologist used the term limbic or emotional brain to one of the three structures that you list in your theory.
Although it is true that today these theories are somewhat out of date and it has been shown that, in reality, emotions are regulated by the whole nervous systemThere is no doubt that there is an important relationship between the limbic system and the emotions.
Limbic system: diseases.
Once we have introduced the limbic system, its parts and functions, it's time to list some of the diseases main.
Being such an important part of our nervous system, there are numerous disorders associated with the limbic system, among the most common we highlight the following:
- Schizophrenia: many studies show that this disease is related to a marked decrease in the hippocampus. Therefore, this disorder also causes memory and learning disorganization. We discover you here what is schizophrenia.
- ADHD: A part of the scientific community affirms that this type of attentional disorders arise in people with an enlarged defect in the hippocampus and tonsils area. They argue that, with so many overexcited neurons, children have behavioral and emotional disinhibition.
- Limbic encephalopathy: patients with this disease often have long-term memory loss, behavioral changes, and in some extreme cases, seizures. Encephalopathy may have subtle symptoms at first, but it usually progresses quickly. However, it has a good prognosis and good treatment can guarantee full recovery.
- Psychomotor epilepsy: neurons located in the hippocampus area are injured producing this type of disease so characteristic. It affects the temporal lobes and its symptoms vary between spelling defects (writing in too large or small letters) and sexual dysfunctions.
Explanatory video about the limbic system.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Limbic system: parts, functions and diseases, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.