The brain is the most important organ in our body. This is made up of different parts, each with different functions. The substantia nigra is one of those parts and in it are the neurons the brain cells that transmit and conduct the neurotransmitter known as "dopamine". This is in charge of the functions related to reward, addiction and movement. Therefore, the black substance is of utmost importance. In addition, it is part of what is known as the basal ganglia (although it is not considered to be an exact nucleus basalis) and is located in the center of the brain.
In this Psychology-Online article, we tell you what is the black substance and what is its function. Discover what it is like, the different functions it has and its relationship with dopamine and Parkinson's.
Index
- What is the black substance like?
- What are the functions of the substantia nigra?
- Relationship between the substantia nigra, dopamine and Parkinson's
What is the black substance like?
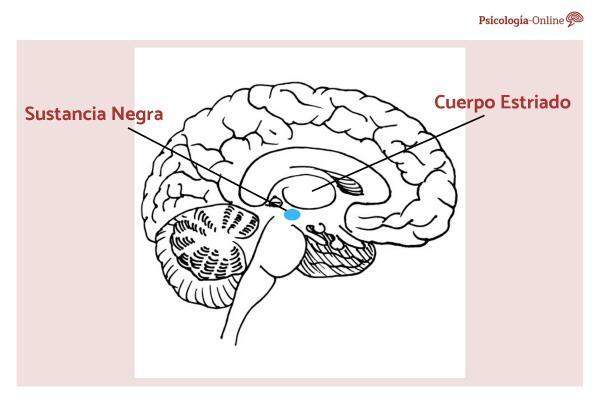
What is the substantia nigra of the brain and what is its function? It is a group of neurons located in the part of the brain known as the midbrain and is part of the basal ganglia. If you wonder what the black substance is like, it is dark in color due to the high amounts of neuromelanin it contains. The substantia nigra of the brain is, in turn, divided into parts with different functions:
- Compact part: serves as an input and to transmit signals to the rest of the basal ganglia. So through the compact part, dopamine can reach the striatum. Because this area has more neuromelanin, it is the darker of the two.
- Reticulated part: this, on the contrary, is the outlet of the basal ganglia and from it the information is sent to other parts of the brain.
In this section we have seen where the substantia nigra is located, and then we will see what the function of the substantia nigra in the brain is. In addition, in the following articles, you will find information about how the human brain works and the parts of the brain and their functions.
What are the functions of the substantia nigra?
As we mentioned, the black substance has two parts and, each of them, has different functions, most of them falling on the compact part. However, the reticular part is important for neuronal inhibition and for eye movements. Next, we will see what are the functions of the black substance of the brain:
- Reward- Substance nigra, and specifically dopamine, is important for reward-related sensations. This is that, after performing a certain activity, we have pleasant sensations, that is, we feel rewarded. This will make us repeat this action in the future in order to obtain said reward. This would explain the functioning of motivation, sexual pleasure or addictions. It is, therefore, related to learning.
- Learning: Due to these reward mechanisms, we repeat the same action. Therefore, we learn to perform a certain behavior. For example, we learn to exercise on a daily basis because we release dopamine and we feel better.
- Fine motor: One function of the substantia nigra of the brain is that it participates in the control and initiation of fine movements. Dopamine and its circulation pathways or dopaminergic pathways participate in this type of movement.
- Temporal perception: the black substance also has a role in the perception of time, especially with regard to the time elapsed between two stimuli.
- Eye movements: As we mentioned at the beginning, eye movements depend on the black substance, specifically on the reticular part. This is responsible for the correct execution of the saccades of the eyes and the stabilization of the gaze at one point despite the movement of the head.
- Sleep regulation: the neurons that are responsible for transporting dopamine participate in the proper functioning of the REM phase of sleep.
Relationship between the substantia nigra, dopamine and Parkinson's.
As well we have gone previously article, in the black substance of the brain is and is transports dopamine and this one has a important role in fine mobility. This refers to the small movements we make on a daily basis, such as picking up a spoon. That is why damage to the dopaminergic pathways causes one of the most characteristic symptoms of Parkinson's: hand tremor.
Likewise, the damage in the substantia nigra and, therefore, in the dopaminergic pathways, also influence other symptoms of the Parkinson's such as muscle stiffness or slowness in movement, sleep problems, low mood, as there is no sense of reward. Yet Parkinson's disease is precisely this: deficit of dopamine secretion and the consequences that this deficit can cause.
To this day, it is not known for sure what can cause this neuronal degeneration, which currently does not have the possibility of recovery, although if it has been possible to delay the deterioration. Everything seems to indicate that the origin is a combination of biological and genetic factors. In general, it is treated with drugs such as levodopa, which is the metabolic precursor of dopamine. That is, the treatment of the disease is based on increasing the amount of dopamine of the substantia nigra of the brain.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the substantia nigra of the brain and what is its function?, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Carpenter, M.B. (1994). Neuroanatomy. Fundamentals. Buenos Aires: Editorial Panamericana.
- Lima, M. M. S., Andersen, M. L., Reksidler, A. B., Vital, M. TO. B. F. & Tufik, S. (2007). The role of the substantia nigra pars compacta in regulating sleep patterns in rats. Public Library of Science, 2(6), e513.
- Nolte, J. (1994) The Human Brain: An Introduction to Functional Anatomy. Madrid: Mosby-Doyma.