Have you ever stopped to think how does our brain work? Is awesome Observe that the small substances found in our brain are responsible for our actions and our well-being.
Dopamine and serotonin are two of the many neurotransmitters found in our nervous system. Dopamine has been recognized as the neurotransmitter of pleasure, while serotonin is associated with the hormone of happiness.
These two small neurotransmitters have numerous functions in our body. Do you want to know what they are? So, keep reading this Psychology-Online article, where we will explain the differences between dopamine and serotonin, what are they and what functions do they have.
Index
- What is dopamine?
- What functions does dopamine have?
- What is serotonin?
- Serotonin functions
- Dopamine and serotonin: differences
What is dopamine?
The dopamine It is a chemical transporter of our central nervous system, that is to say a neurotransmitter. Neurotransmitters have the function of connecting neurons
This neurotransmitter activates five cell receptors (from D1 to D5) and its activation gives rise to the different functions of dopamine in our body. Although it is generally known as the neurotransmitter linked to sensations of pleasure and as an activator of the reward systems, it has been involved to a great extent in the global functioning of the brain, having an implication in the emotional, cognitive and affective processes. In addition to being linked to the sensation of pleasure, among its functions we also find involvement in the motivation, movement coordination, decision-making, learning, emotionality, and affectivity.
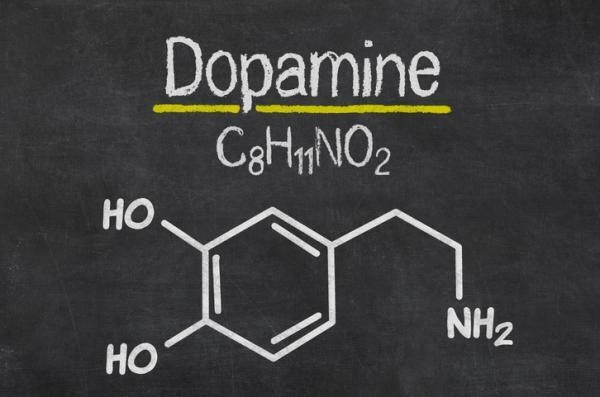
What functions does dopamine have?
Dopamine is one of the neurotransmitters most important parts of the brain and, therefore, it is involved in several functions. Its involvement in multiple functions is due to the fact that this neurotransmitter is distributed throughout the different brain regions, allowing its action in multiple functions with very different activities, such as:
- The movement: dopamine is involved in the production of motor movements and therefore optimal levels of this substance are necessary for motor function. A deficiency of dopamine in the basal ganglia, which allows movement, would reveal the Parkinson's disease, as well as hyperactivity of dopamine could cause hyperkinetic disorders, such as the nervous tics.
- Cognitive processes (memory, attention and learning): the presence of this substance in the hippocampus and the cerebral cortex produces an implication in the memory, attention and learning. That is why in the face of a dopamine deficit in our body, the person may experience a deterioration in memory, attention and learning processes. It is known that people with a attention deficit disorder they maintain lower levels of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex.
- Feeling of pleasure: Obtaining pleasure or reward is perhaps the most commonly known function of this substance. Dopamine is also secreted by the limbic system, which allows sensations of pleasure to be experienced. When we do an activity that we like, there is an increase in the release of dopamine, which causes us to obtain feelings of pleasure and reward. In the same way, there are substances such as drugs or food and actions such as sex, which increase the secretion of dopamine and therefore, these are abused. Some drugs such as cocaine or amphetamines inhibit the body's function on the re-absorption of dopamine, thereby causing a higher concentration of dopamine in our body, causing more sensation of pleasure and an increased possibility of addiction.
- Decision making: high amounts of dopamine are found in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, which is responsible for the executive functions. For this reason, a deficiency of the substance in this region produces a cognitive flattening, as happens in the schizophrenia, where the person loses the ability to react to external inputs, generating great difficulties in decision-making.
- Sleep regulation: Dopamine is in charge of telling us that we are sleepy when we have not been sleeping for hours, due to its involvement in the circadian rhythm, with the release of melatonin. For this reason, it is involved in the regulation of sleep.
What is serotonin?
The serotonin, like dopamine, is a neurotransmitter of our nervous system, known chemically as 5-HT, which is found primarily in the brain, intestines, and blood platelets.
This hormone is commonly known as happiness hormone, due to its involvement in emotions and mood, so that together with other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and adrenaline, it regulates our mood. However, it has also been implicated in appetite control, as a precursor to melatonin helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle and intervenes in libido and sexual desire, among others functions.
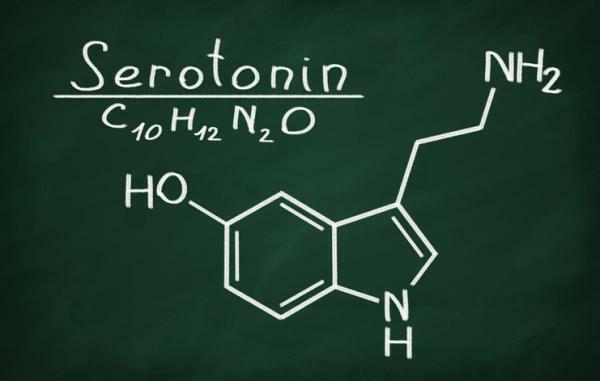
Functions of serotonin.
Like dopamine, serotonin is found in different regions of our brain, thereby causing its involvement in very different actions. For this reason, it is very important to maintain adequate and balanced levels of this hormone in our body. Let's see what its most representative functions are:
- Involvement in digestion: high amounts of serotonin are found in the stomach and intestines, which causes it to be involved in the control of the function of the intestine and its movements. High levels of this hormone in the intestine are related to the appearance of diarrhea, while its deficit is linked to constipation. Its activity in this region of the body is also related to an increase or decrease in appetite.
- Mood regulation: Serotonin is known as the happiness hormone because it affects mood, the appearance of anxiety and the happiness. For this reason, low levels of serotonin have been linked to the onset of depression and illegal drugs that increase their levels, such as ecstasy or LSD, produce an alteration in the state of cheer up. In this article you can see the relationship between serotonin and depression.
- Sexual function: serotonin has a great implication in sexual desire. Faced with low levels of serotonin, there is an increase in desire, while high levels are associated with its inhibition.
- Sleep regulation: Like dopamine, this hormone fulfills its function in the regulation of sleep, due to its involvement in the circadian rhythm and the control over the secretion of melatonin.
- Body temperature: Serotonin helps regulate our body temperature, performing maintenance functions on temperature. This function is very important because the variation of a few degrees in our body temperature can lead to the death of many cellular tissues in our body.
Dopamine and serotonin: differences.
Serotonin and dopamine, as neurotransmitters found in our body, have a very important role in our well-being and although they can maintain similar functions, there are several differences found between both of them:
1. The production
The first difference that must be established between the two neurotransmitters is their synthesis. Serotonin is synthesized from amino acid tryptophan, while dopamine is synthesized from the tyrosine.
2. emotional states
Dopamine plays an important role in energetic emotions, such as motivation, pleasure, arousal or euphoria, while serotonin plays the opposite role, producing feelings of calmTherefore, a deficit of this hormone is related to the appearance of anxiety and depression.
3. Pleasure and happiness
Although the presence of these two neurotransmitters in our body give off positive feelings, dopamine has been associated with sensations of pleasure, while serotonin has been linked to happiness.
4. Low levels
There are differences between the two in the consequences that are seen in our body in the event of a deficit of these substances. Faced with a dopamine deficit, disturbances in memory, learning and concentration, in the movement e inhibition of sexual desire. While serotonergic deficits cause irritability, insomnia and a high sensitivity to pain.
5. Body function
Although the two neurotransmitters have been suggested to be involved in body movements, dopamine deficiency has been clearly related to appearance of stiffness in the extremities or the appearance of Parkinson's disease, while the role of serotonin in body movement has not been defined.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Differences between dopamine and serotonin, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Bahena-Trujillo, R., Flores, G., & Arias-Montaño, J. TO. (2000). Dopamine: synthesis, release and receptors in the Central Nervous Systeml. Revista Biomédica, 11 (1), 39-60.
- Delgado J.M., Ferrús A., Mora F & Rubia F.J. (1997). Neuroscience Manual. Madrid: Synthesis.
- Estevinho, M. F., & Soares-Fortunato, J. M. (2003). Dopamine e receptors. Portuguese Journal of Psychossomatic, 5 (1).
- Lacasse, J. R., & Leo, J. (2006). Serotonin and Depression: A Disconnect Between Advertising and Scientific Literature. College of Social Work Faculty Publications, 43.
- Pedraza, C., Navarro, J., & García, F. (2005). Involvement of dopamine in the cognitive processes of learning and memory. Biological Psychiatry, 12 (6), 232-236.
- Rivera, J & Haddad, J. Serotonin and syndrome. Rev. Med Hond, 32.6.
- Trueta, C., & Cercós, M. G. (2012). Regulation of serotonin release in different neuronal compartments. Mental Health, 35 (5), 435-443.
- Vargas-Barahona, L. M. (2007). Parkinson's disease and dopamine. BUN Synapsis, 2 (2), 11-15.