There are many theories about how our mind works and how the brain regulates these mental processes. In recent decades, the many advances in neuroscience have allowed us to discover new ways of understanding the brain and how it works.
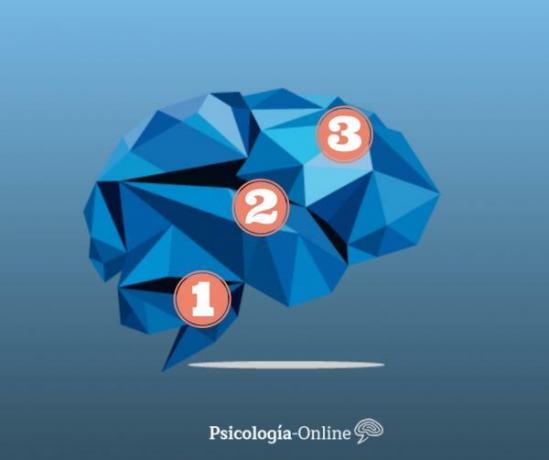
In 1990, Paul MacLean proposed a brain structure divided into three brain systems (commonly known as the three brains) interconnected with each other, he defined each structure and created the known triune brain theory or triune brain. These systems are divided as follows:
- Reptilian brain
- Limbic or emotional brain
- Rational brain or neocortex
Do you want to know more about MacLean's Triune Brain Theory? Then do not miss this interesting article that we offer you in Psychology-Online.
Index
- The Triune Brain Theory
- The reptilian brain
- The emotional or limbic brain
- The rational brain or neocortex
- Criticisms of the triune brain theory according to psychology
The Triune Brain Theory.
The triune brain theory or
In essence, the three-brain theory proposes a novel way of regrouping our brains. These three blocks or sections are known as the reptilian brain, the limbic or emotional brain (coinciding with the limbic system) and the rational brain.
These sections are connected to each other but in turn function independently. Therefore, information is constantly sent despite each being focused on a specific function.
Paul MacLean: biography, theory and books
Born in 1913 in the United States, Paul MacLean He was a physician focused on the field of neurosciences who devoted much of his studies to the field of psychology and psychiatry. He began to develop his theory inspired by the neuroscientific texts of papez and proposing the limbic system as the center of emotions.
From these small steps, Paul MacLean developed a theory that would take hold in the late 1970s. However, it was not until 1990 that his studies on the theory of the triune brain were embodied in the book known as "the triune brain in evolution".
Next, we will develop the three systems defined by MacLean according to their triune brain theory
The reptilian brain.
Also known as the instinctual brain or basic brain, this is the most primitive brain of all according to MacLean's theory.
The reptilian brain is considered as the ancestral structure that regulates our vital functions and the most instinctive behaviors related to individual survival (eat, drink, sleep) and of the species of him (urges and sexual relations). Ultimately, according to psychology, the function of the reptilian brain is to act quickly and instinctively to ensure our survival.
Reptilian Brain Anatomy
We found the reptilian brain in the lower brain area: the brainstem and forebrain (1). The reptilian brain according to psychology is that area in which the energy levels of our body are controlled and balance is sought, also known as homeostasis.
Many experts claim that the amygdala is part of the reptilian brain, however, the debate remains open as to whether this organ is part of the limbic system or the instinctive brain.

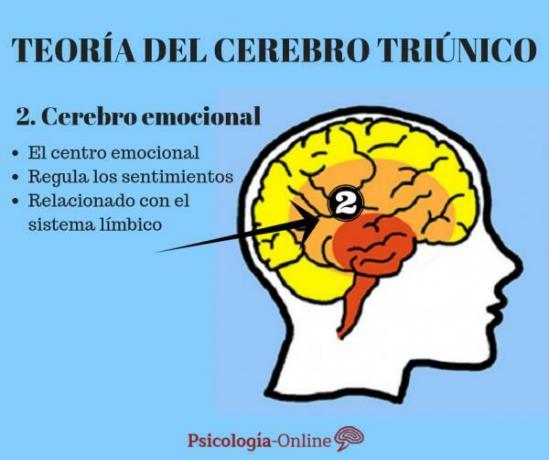
The emotional or limbic brain.
According to the triune brain theory, this area appeared with the first mammals and developed above what we have previously defined as the reptilian brain. The limbic brain is considered the center of emotions, that is to say: our emotional nervous system. And it is responsible for producing and generating emotions in our nervous system.
It is important to state that this area has a highly adaptive function: produces emotional responses and generates very important learning at an experiential level. Our memory, motivation, activation, and attention systems tend to function more productively when influenced by emotions.
- Let's take an example: we will remember an event better if we have felt a strong emotion (such as going to the concert of our favorite group). Instead, we tend to forget those events that do not produce intense emotional responses.
Relationship between emotional brain and limbic system
This second structure is constituted in turn by six elements: the thalamus, the amygdala, the hypothalamus, the olfactory bulbs, the septal region and the hippocampus. Coinciding with what we define today as limbic system (2).
The limbic system, like the emotional brain, is the area in charge of regulating emotions and modulating the way we express them.
The rational brain or neocortex.
Finally, according to this interesting theory of the three brains, we find ourselves with the neocortex or rational brain: this part of our brain is in charge of cognitive processing and decision making reasoned and logical.
Popularly, the rational brain is called gray matter, however, the neocortex is made up of various encephalic structures, among them we highlight the left hemisphere and right hemisphere of the cerebral cortex. Another name by which we find this area is the isocortex.
Functions of the neocortex
We must understand the rational brain as a structure practically unique in our species. According to MacLean, humans are the only organism that has a fully developed neocortex.
- The abilities intellectual, logical and decision making Rational are some of the abilities that this cerebral zone provides us.
- In addition, the rational brain also helps us in the processes of self-awareness, reflection and organization.
Anatomically speaking, we find the neocortex in the most superficial area of the encephalon (3), it makes up 90% of the cerebral cortex and extends in the form of folds and circuits.

Criticisms of the triune brain theory according to psychology.
The nervious system it is a complex network of neuronal cells that work as a team. Although we can differentiate different parts of the brain and nervous system anatomically, the MacLean model it's too simple for all the information we have today.
Still, the triune brain theory is very important since it relates brain areas to specific mental functions. Thanks to this theory (among others) today, we can develop some disciplines such as neuropsychology.
The triune brain theory in neuromarketing
Although the triune brain theory in marketing has a lot of impact, in psychology it is considered an outdated model. Thanks to new neuroimaging techniques, we can see that our brain is not made up of parts as if it were a puzzle.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to MacLean's Triune Brain Theory, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.
References
- MacLean, Paul D. The triune brain in evolution: Role in paleocerebral functions. Springer Science & Business Media, 1990.
Bibliography
- Velásquez Burgos, B. M., Calle, M. G., & Remolina De Cleves, N. (2006). Neuroscientific theories of learning and their implication in the construction of knowledge of university students. Tabula Rasa, (5).
- Patiño, M. (2008). Know your brain. Bogotá: Metropolitan Technological Institute.


