To understand what a mental illness or disorder We must be aware of its origin and what are the characteristics of these, since it has been lent to confusion and some share certain characteristics (psychosis) that generates confusion and many times a bad treatment.
Then the need arises for the exchange of information about what mental illnesses are, therefore the lack of this creates a great labyrinth and disinterest, coupled with total ignorance that results in stigma, isolation and marginalization of the person who suffers them, That is why the term Mental Illness has fallen into disuse and some authors prefer to call this type of illness "Disorders or Disorders Mental ”.
In this Online Psychology article we are going to discover the characteristics and differences of mental or psychological disorders.
Index
- Causes of mental or psychological disorders
- Classification of mental disorders
- Neurotic disorders
- Psychotic disorders
- Differences between neurosis and psychosis
Causes of mental or psychological disorders.
We must consider that mental disorders or psychological disorders are the mental condition in which they are shown altered cognitive and affective processes development, this is considered abnormal in relation to the social group where the individual develops, these are related to the change of character and emotions, but they can also be Congenital, they have a specific pathology with signs and symptoms, Genetic and hereditary.
- Congenital: Are those produced by disorders in embryonic development during pregnancy due to various causes (rubella, syphilis, herpes, toxoplasmosis, alcohol, tobacco), due to environmental factors (radiation) or during the delivery
- Genetics: Are those produced by damage to the genes or chromosomes. The nervous (Down syndrome), respiratory (asthma), digestive (type 1 diabetes, cancer), visual (color blind), and blood (hemophilia, lymphoid leukemia) systems are affected. On the other hand, they can lead to the appearance of cancer in various organs. Genetic diseases may or may not be heritable. When they are inherited they are called hereditary diseases.
- Hereditary: It is a set of genetic diseases that are transmitted to offspring, although they are not necessarily observed at birth. In addition, these diseases may or may not manifest themselves throughout the life of the individual (diabetes, breast cancer).
There are several ways of referring to mental illnesses, among which are the called Mental Disorders among which are, the psychological, psychiatric, problems mental, etc.

Classification of mental disorders.
There are numerous ways to classify mental illnesses, which can be more or less serious both individually and socially; a classic classification is that of: Neurotic Disorders and Psychotic Disorders.
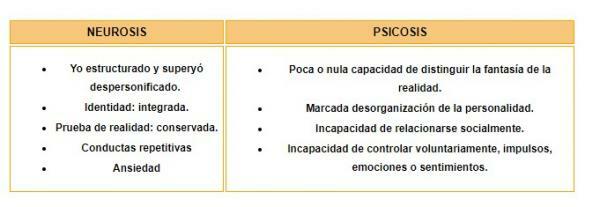
- Neurotic disorders: depressive, anxiety, dissociative (multiple personality), sexual (fetishism, masochism) and sleep (insomnia) disorders, without a demonstrable organic alteration (according to WHO)
- Psychotic disorders: includes states of schizophrenia, delusions and hallucinations, as well as states produced by certain diseases or substances that enter the body.
As previously discussed, some illnesses such as those that produce psychotic states have some similarities, but meet different criteria, equally and in no way should terms such as psychopathy be mistaken with the states psychotic.
Neurotic disorders
Is all that mental disorder arising from anxiety and whose symptoms infer normal activity but do not block it (Freud)
In clinical psychology it is used to refer to mental disorders or illnesses which distort rational thinking and functioning adequate level of people at the family, social and work level, without evidence of organic injury and adequate level of connection with reality, this type of Diseases do not require hospitalization, and their treatment is done in an outpatient clinic, with the exception of personality disorders that sometimes requires this.
Ethylogy
The term was proposed by the Scottish physician Willian Cullen in 1769 and refers to diseases or disorders of the system nervous, which did not show organic damage which could be demonstrated, but capable of altering the emotional and physical state of the individual.
Between 1892 and 1899 S. Freud calls it Psychoneurosis which is applied to nervous diseases whose symptoms represent a repressed conflict; psychoanalysis I use it to refer to almost any mental disorder, and I exemplify it with cases of hysteria in women which allowed Freud, the development of the theory psychoanalytic.
In 1909 Pierre Janet published the neurosis. Work in which he establishes the concept of "functional disease", which does not have a physical alteration of the organ but of its function, which causes a state of neurastastenia (nervousness).
The term Neurosis has been abandoned by scientific psychology and psychiatry, the WHO (ICD 10) and the A.P.A (DSMIV TR) has changed the nomenclature to refer to these clinical pictures and I call them Disorders.

Psychotic disorders.
Psychosis is a term widely used in psychology to refer to a mental illness where your main characteristic is the loss of contact with reality, people who suffer from this condition are called psychotic, and present hallucinations, delusions, changes of disorganized personality and thinking, have an inability to adapt to daily life and difficulty interacting socially; with or without organic damage.
Stedman's Medical Dictionary defines psychosis as "a severe mental disorder, with or without organic damage, characterized by a personality disorder, loss of contact with reality and causing worsening of social functioning normal".
At the moment only the nosological classification of DSM IV is accepted, as descriptive the German school of Bleuler, Kraepelin and Kleist, and as for the description of delusions the French school influencing as an exponent Gaetán de Clerembault
The hallucinations of this type of disease are mostly auditory although they also usually appear visually, as well as false beliefs of what one is or what is happening.
Some people mistakenly call psychopathies, which is why their characteristics and symptoms are confused.

Differences between neurosis and psychosis.
The confusion that occurs when the terms are used incorrectly has been mentioned earlier as some people use the term psychopathic to refer to a psychotic person.
When we refer to psychopathic, we are in front of an individual with antisocial personality, who treat people as if they were objects and use them for their own benefit, they lack empathy and if they do, it is only used to grasp the needs and weaknesses of the other and use them to be able to manipulate him, he never provides anything and when he does he hopes to recover it subsequently.
However, a psychopath is not always a serial killer as society knows him today, he is a person who is capable to be nice and adapt to society but do not hesitate to commit a crime, without feeling remorse or guilt. These individuals follow their own code and rules and may feel bad when they break, they lack the superego which represents the ethical and moral thoughts received from the culture. And they are not amenable to psychotherapy.
Instead the psychotic person, is iunable to relate socially and has no will with respect to feelings, they have strange behaviors, in addition to that this disorder can be functional or organic, and if it can be controlled with psychotherapy and antipsychotic or neuroleptic drugs, reaching the individual to function socially.. It should be noted that the treatment of this type of disorder will depend on the cause of it.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Mental or psychological disorders: characteristics and differences, we recommend that you enter our category of Clinical psychology.


