Inventory control takes care of minimizing the total cost of inventory. In the engineering world the term often used is inventory control.
The three main factors in the inventory control decision-making process are:
Advertisements
- The cost of maintaining products (for example, based on the interest rate).
- The cost of making a order (for example, for raw material stocks) or the cost of starting production.
- The cost of the shortage, that is, what is lost if the stock is insufficient to satisfy all the demand.

The third element is the most difficult to measure and is often handled by establishing a policy that can be called 'service level«, For example, a certain percentage of the demand will remain uncovered if we are left without stock.
Advertisements
Some important concepts
The ABC Classification: The ABC classification system is to group items according to the annual volume of sales, in order to identify the small number of elements that represent the largest part of the sales volume and that are the most important for the control of the efficient management of the Inventory.
Advertisements
Reorder Point (ROP): It is the inventory level when an order must be placed to replenish a product. The inventory level R is calculated: R = D * L, D = product demand (per day, week, etc.), and L = supplier lead time. In other words, if we know that the company that produces "bread" consumes 5 bags of flour a day and the supplier takes 3 days to bring the requested product, we know that when we have 15 bags we must place the next order.
Optimal order quantity: It is the amount that we must request from our supplier in order to optimize the costs involved. This method involves many other variables that the inventory manager must consider. The formula to calculate this value is:
Advertisements
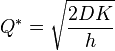
Where:
Advertisements
Q ^ * = optimal order quantity
D = annual amount of demand
K = fixed cost per order
h = annual storage cost per unit.
Security stock: It is the difference in inventory between the times when an order is placed and when the new stock is received. If there are not enough products then a shortage may occur. Continuing with the previous example, we should not wait to have the 15 bags of flour to place the new order, but we must have a quantity in safety stock, always thinking in the event that the supplier is late in its delivery or demand increases and more bags of flour are occupied in the factory.