Drugs are those substances that modify the normal functioning of the nervous system and create addiction. Currently, drug use is considered a major health problem in the population. However, not all drugs are the same or produce the same effects. What types of drugs are there? There are different types of drugs, grouped according to different classification criteria. How are drugs classified? In this article from Psychology-Online: classification of drugs according to the WHO and their effectsWe will delve into the main classifications used to group drugs, especially in the classification proposed by the World Health Organization.
Index
- What are drugs
- Classification of drugs
- Types of drugs according to legality
- Classification of drugs according to the effect on the CNS
- Popular drug classification
- Types of drugs according to psychoanalytic models
- Drug effects
- Classification of drugs (WHO): summary scheme
What are drugs.
What is a drug? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "a
Let's break down this definition of drugs given by the WHO:
- Drugs are substances, therefore, drug addictions are addictions to a substance. However, there are other behavioral addictions, such as pathological gambling.
- They are all substances that affect the CNS and create dependence. These substances can be both natural and artificial, and also legal or illegal.
- They can be introduced into the body by any route of administration. That is, they can be ingested orally, they can be smoked, they can be injected to be introduced intravenously, and they can also be "snorted" or inhaled through the nose.
- They alter the central nervous system, therefore, they can excite, they can calm, they can calm pain or they can distort the perception of reality.
- They create dependency, that is, all drugs have the capacity to generate dependency. Dependence is understood as the need to consume the drug and presents a series of symptoms that indicate that the person has lost control over the consumption of the substance and continues to consume it even though he is aware of its consequences adverse.
Classification of drugs.
How are drugs classified? Psychoactive drugs or substances can be classified according to different parameters, such as, for example, according to their origin or origin, according to its structure, its effects on behavior, its danger to health or its impact Social. As we can see, there are different criteria for grouping drugs, but in this article we will focus on the most accepted classification and other common classifications:
- According The effect that produce substances in the central nervous system, the most appropriate classification according to the WHO.
- According legality to produce, possess, trade or consume the substances.
- According the dangerousness of substances, a popular classification.
Types of drugs according to legality.
A classification of drugs is based on the criterion of the legality of the substances. Legality refers to the legislation of each country. In this way, we find two main types of drugs:
Legal drugs
Legal drugs are those psychoactive substances that are allowed, that is, whose use is not penalized by law. The legality of drugs varies according to the laws of each country, in addition, the consumption of said substance may be legal but not the sale of it.
On the other hand, the legality of drugs does not correspond to their dangerousness. Although they are legal, drug abuse is dangerous and harmful to health. So much so, that in our society, the drugs that are most consumed and the most health problems entail are, precisely, legal drugs such as tobacco and alcohol. Legal drugs are:
- The alcohol. This is the drug that has the greatest social acceptance. In Spain, its consumption is only legal after 18 years of age.
- Nicotine. Tobacco is one of the most widely used drugs. Here you can see the effect of nicotine on the nervous system. Generates dependency, which can be evaluated with the Fagerström test.
- The caffeine. Caffeine has effects on the nervous system, therefore, it can be considered a psychoactive substance. However, its effects are much less and its consumption in normal amounts is not dangerous. Caffeine is mainly found in coffee, but also in soft drinks.
- Theobromine and theophylline. Like caffeine, they are not dangerous in normal amounts. They can be found in tea and chocolate.
- Drugs. Mainly, psychotropic drugs, which alter the CNS. Among them are benzodiazepines and amphetamines (by prescription). The use of drugs is medicinal and should be used with medical supervision.
Illegal drugs
Illegal drugs are those psychoactive substances whose use it is not allowed by the law of the country. It may be that own consumption is allowed in some circumstances, but the sale is penalized. Illegal drugs are all other drugs. Among the most commonly used illegal drugs are:
- Marijuana. It is considered the most widely used illegal drug. It is obtained from the hemp plant called cannabis sativa. Its active ingredient is tetrahydrocannabinol. Here you can see the symptoms and treatment of marijuana addiction.
- Hashish. It is obtained from the resin of the same plant and shares the same active principle.
- Cocaine. This illegal drug is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant called erythroxylum coca. In addition to consuming it, it is also illegal to both grow it and sell it.
- MDMA. It is known as ecstasy and is illegal due to the dangers and serious health consequences associated with its use.
- Amphetamines or speed. They are considered illegal when used without medical supervision for recreational purposes.
- Heroin. It is illegal to make, sell, and be in possession of this substance. It was made illegal after observing its serious consequences.
- Phencyclidine or PCP. Although it had been used for pain relief, today it is an illegal drug.
- LSD or lysergic acid diethylamide. It had a psychiatric use, but it was outlawed due to its hallucinogenic effects.
- Ketamine. It was used for anesthetic purposes, but it was also outlawed due to its hallucinogenic effects.
- The popper or amyl nitrite. It is a vasodilator that was made illegal after being consumed for reacreative purposes.
- Magic mushrooms. They contain psilocybin and psilocin and are illegal because they cause hallucinations.
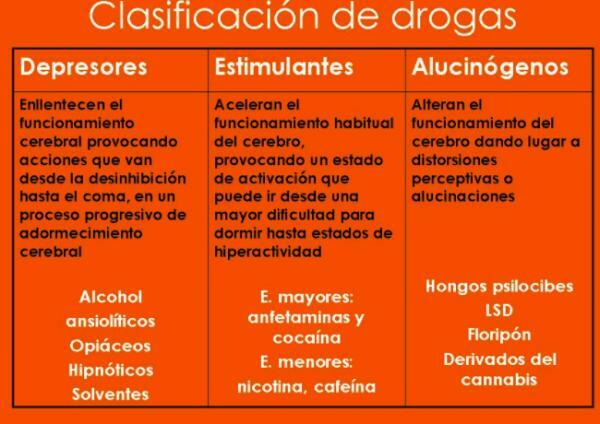
Classification of drugs according to the effect on the CNS.
Grouping substances according to their effect on the central nervous system is considered the most correct way to classify drugs. This classification is the one proposed by the World Health Organization and separates psychoactive substances into depressants, stimulants and disturbing substances. The three types of drugs are explained below:
Depressant drugs
Depressant drugs are substances that they decrease the activity of the CNS. They do this by repressing presynaptic structures, reducing the amount of neurotransmitter, also reducing the function of postsynaptic receptors. The main groups of CNS depressant substances are:
- Sedatives / hypnotics
- Opiates
- Neuroleptics
Some examples of depressant drugs are:
- The alcohol
- Cannabis
- Benzodiazepines
- Heroin
Stimulant drugs
Stimulant drugs are substances that they stimulate the activity of the CNS. They do this by blocking inhibition or by directly exciting neurons. The stimulation is explained by the increase in neuronal depolarization, the increase in the amount of neurotransmitters (NT) available, the lengthening of the action of NTs, the weakness of the neuronal membrane and the decrease in synaptic. In this way, they can cause symptoms such as tachycardia, pupillary dilation, sweating, increased blood pressure, and so on. They can also be called sympathomimetics. Stimulant drugs are as follows:
- Amphetamines
- Cocaine
- The caffeine
- Theobromine and theophylline
- Nicotine
Disruptive drugs
CNS-disturbing drugs are those substances capable of modify psychic activity and produce alterations in perception such as hallucinations, as well as alter mood and thought processes. Some examples of disruptive drugs are:
- LSD
- Hallucinogens
- Cannabis
- MDMA
- Ketamine
Popular drug classification.
There is a popular and colloquial way of classifying drugs into two types: hard or soft. This classification is made according to their perception of danger and social and health impact. However, this classification not considered adequate as it is misleading by underestimating risk alcohol, tobacco and cannabis.
Soft drugs
The drugs considered soft are those that are more socially accepted, since they are perceived as less harmful. Something totally misleading, as we have already commented before, tobacco and alcohol are the drugs that involve the most health and human costs. Although some of the soft drugs do not produce physical dependence, they do produce psychological addiction. Soft drugs are considered to be:
- Tobacco
- The alcohol
- Marijuana
- Hashish
- Anabolic steroids
- The caffeine
- The popper
Hard drugs
Drugs considered hard are perceived to have a greater social and health impact, since their consumption is more dangerous in the short term. To this type of drugs correspond:
- Psychotropic drugs
- Heroin
- Morphine
- Cocaine
- Amphetamines
- MDMA or ecstasy
- LSD
- Magic mushrooms
- The PCP
- Ketamine
- Barbiturates
- Methadone
Types of drugs according to psychoanalytic models.
Following this criterion, they proposed the following types of drugs:
- Alcohol and barbiturates.
- Amphetamines.
- Cannabis (marijuana, hashish).
- Cocaine.
- Hallucinogens (LSD and the like).
- Opiates
- Volatile solvents (glues, industrial products)
- Tobacco.
In the models with higher rates of rehabilitation and maintenance of drug abstinence and alcohol, psychoanalytic positions are not used and the classical positions of S. Freud and J. Lacan because they are systems of prolonged psychotherapies, which do not have the psychological objective of changing behavior or eliminating a habit or addiction and therefore their effectiveness is further limited.
The complication of psychoanalytic treatment causes that in the approach to cocaine addiction, specialists use creativity and improvisation in many situations to try to provide help to the patient. The results achieved by the psychodynamic currents have been unfortunate, their theory and methodology it is not configured for the treatment of human disorders and disorders of these characteristics. We have known considerable cases of psychiatrists and psychoanalysts who attempt treatment psychology of drug users with the same psychodynamic methodology, without getting them to abandon consumption.
During the psychotherapeutic approach of a drug addict or abuser, the first objective is the necessary urgency that exists to stop the consumption of the drug. substance, this is the priority because while the subject consumes any drug or cocaine, his health and that of other close people and outsiders is at risk. he. It is very useful and cannot be postponed to guide and work with the person's present because it will be the only thing that can be handled and modified, for example, with the cognitive behavioral therapy techniques.
Drug effects.
Drugs are chemicals. When consumed, they reach the bloodstream and from there travel throughout the body, including the brain. When they reach the brain, the drugs can have different effects. As we have seen in the previous sections, we can differentiate between three types of drug effects on the brain or CNS: they can stimulate, they can relax or they can alter the senses.
- The effect of drugs stimulants is to produce the feeling of being awake or having great energy, as well as euphoria, disinhibition, lack of emotional control, aggressiveness, lack of feeling of fatigue, psychomotor excitement and irritability.
- The effect of drugs depressants it is sedative thus, therefore, they affect by decreasing the perception of stimuli, relaxing and providing the feeling of well-being and tranquility.
- The effect of drugs disturbing or hallucinogenic are distortions in perception, alteration of mood and thought. They cause the alteration of the senses so that you can have unreal sensations.
There are many types of drugs and each drug produces its specific effect. Broadly speaking, we can say that most drugs produce drug addiction, although this is not the only danger. The drug addiction it has many consequences. Drugs negatively affect the ability to make decisions, which causes risky behaviors under their influence. In general, drugs they can cause illness, mental problems, family, social, legal problems and even death. For all this it is so important prevent drug addiction.
Classification of drugs (WHO): summary scheme.
This table is a schematic summary of the classification of drug types according to the World Health Organization, perfect for study or review.

This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Classification of drugs - WHO and its effects, we recommend that you enter our category of Addictions.
References
- World Health Organization (2004): Neuroscience of psychoactive substance use and dependence.
Bibliography
- Beríritu Villalobos, L. (2010). Drug addiction, drug dependence and drug dependence: definitions, confusion and clarifications. Cuicuilco, 17 (49), 61-81.
- Hourmilougué, M.C. (1997). What is a drug?
- Kramer, J. F., Cameron, D. C., & World Health Organization. (1975). Manual on drug dependence: compiled based on WHO expert group reports and other WHO publications.
- Maturana, A. (2011). Alcohol and drug use in adolescents. Las Condes Clinical Medical Journal, 22 (1), 98-109.


