Gregory Bateson, an American psychiatrist and anthropologist of English origin, studies among the Iatmul of New Guinea where he is and he falls in love with the anthropologist Margaret Mead. The two will lead to an interesting intellectual partnership that will last even beyond their sentimental history. During...
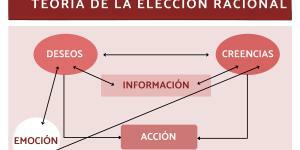
A characteristic of human action is rationality and its more strictly behavioral basis, intentional / conscious action. The philosophy, The social sciences and economics have tried, each with its own instruments, to clarify the concept of rationality and, in the case of economic theory,...

Intrinsic-extrinsic motivation would analyze the propositional aspect of behavior, but would place more emphasis on the analysis of differences individuals based on this motivational variable. Intrinsic motivation is the motive to carry out an action when there is no external reward for it....

In summary, the psychologist Cattell suggested two different forms of intelligence. Fluid intelligence is defined as the ability to solve new problems, use logic in new situations, and identify patterns. Rather, crystallized intelligence is defined as the ability to use...

Murray defined it as the "desire to have friends, establish reciprocal relationships, or cooperate with others." At the behavioral level it is reflected in actions that lead to meeting people, showing friendship, or doing things to please others. It is required to assess the person's desire to associate with...

Eysenck combines the correlational tradition (descriptive or taxonomic model) with the experimental one (causal or explanatory model). The descriptive model speaks of three independent dimensions to describe personality: Psychoticism (P), Extraversion (E) and Neuroticism (N). The causal model links the dimensions...

All of Cattell's work has been aimed at discovering the elements that make up the personality, and developing tests for to be able to value these elements or traits. He has also argued that the way to achieve both goals was the use of FA (Cattell factor analysis)....

The Psychology of Individual Differences addresses the description, prediction and explanation of interindividual, intergroup variability and intraindividual in relevant psychological areas, with respect to its origin, manifestation, and functioning. Description Requires the following steps: Observation...

The active nature of the human being means that it is not a passive receptor of external stimulation, but that it chooses and, to a large extent, generates the scenario in which their behavior will develop. In that sense, people differ in the way in which they categorize the situations in which they find themselves,...

According to Thesaurus, being intelligent involves very basic aspects related to the speed and agility of the mind, as well as very complex processes like reasoning, discernment or understanding... Being smart implies: the ability to acquire and apply knowledge. The ability to think...

The Big Five model proposes the existence of five basic personality factors that supposedly have universal validity. Part of the lexical hypothesis, which defends that, in the different natural languages, the most important personality characteristics have been encoded...
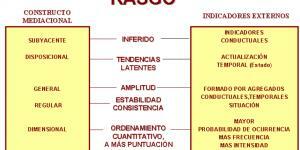
Trait is a scientific concept that summarizes the behaviors that people perform in different situations and occasions. Traits are constructs that allow describing individual differences. According to Eysenck, they are provisions that allow people to be described and their behavior to be predicted. Are not...

When it comes to understanding behavior as a result of the constant interrelation between individual factors and the situation, greater relevance is granted to the subjective dimension of said situation. The subject largely chooses or shapes the type of situations in which her behavior unfolds, depending on, to a large extent,...
Another concept proposed to fill an explanatory gap in the reasons for behavior is style. Style is not conceived as a skill, but in terms of preferences for one or another way of acting (procedural strategies). This term was introduced by Allport from the theory of...

When studying behavior from a dynamic interactive or "transactional" approach, we consider the intervention of personal factors, situations, the interrelationship between the two, the resulting behavior (let's call it 1), its consequences and how these would affect future behavior, perception...

There are various works that provide evidence of the two-phase reaction suggested by Wortman and Brehm, first reactance and then defenselessness. Mikulincer found that with a low training (a failure), the subjects showed reactance (a better performance); while with high training (4...

In clinical and health psychology, one of the most important applications of the model is its use for the diagnosis of disorders of personality. Its supporters consider the dimensions to be continuous (people with disorders have extreme scores on certain dimensions...

In social psychology, attribution is the process by which individuals explain the causes of behavior and events. The development of models to explain these processes is called attribution theory. The attribution theory proposes that the attributions that people make about the...

Historically there is a gap in the role that emotion plays in personality-intelligence dynamics. Perhaps it is due to the fact that emotions are perceived as incompatible with clear and effective thinking (emotion-reason tension). Emotion-reason tension This tension has been very present...

The study of personality must be done taking into account that the person develops in situations, which in turn, are immersed in a certain society or culture. Importance of the study of the situation. It is well known in personality research that the weight of...

Differential Psychology uses the knowledge provided by genetics when it addresses the attempt to explain individual differences on a level of ultimate or distal causes. Numerous studies carried out over the last decades have focused on this issue and whose future discoveries...


