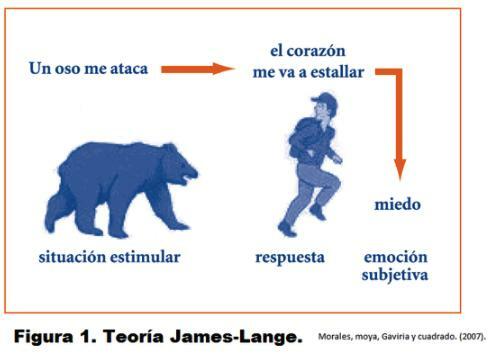
Early theories of emotion were They will consider the mentalistic theory of James and the physiological theory of Cannon. Emotion as a bodily sensation: The James-Lange theory. It is the oldest psychological theory. It was proposed independently by James and Lange. William James He noted that common sense seems to indicate that the perception of a situation gives rise to the feeling of emotion and that a whole series of bodily changes take place.
According James this assessment is incorrect. His theory of emotion proposes just the opposite: it is the bodily changes that immediately follow the perception of an event. Emotion is the sensation of these bodily changes. The basis was introspection. It is not possible to think about emotion without concomitant sensations. Two questions are answered:
- What are the body changes associated with each emotion?
- Why do these connections exist between bodily sensations and emotions?
To answer the first question, he referred to the observations made by Darwin a few years earlier. He responded to the second by stating that many of these changes are not known to be due. The theory leaves more unexplained than it does. Your interest is due to having:
- It was pointed out that emotion is a subjective and personal state.
- It gave rise to research on the influence of changes in the autonomic nervous system on emotion, and in general, to psychophysiological research on emotion.
Cannon's thalamic theory.
He harshly criticized James's theory. The bodily sensations are too slow and diffuse to be able to explain the rapid and profound changes produced by the emotional experience. According to thalamic theory, stimuli reach the cerebral cortex through the subcortical systems. The thalamus informs the cerebral cortex, and both emotional experience and peripheral body changes take place. It is a subcortical neurophysiological theory, especially thalamic. When a stimulating situation excites the receptors, they send their messages to the cerebral cortex that stimulates the thalamus.
It reacts by producing the different emotions. The changes produced in the viscera cannot be responsible for the emotions. Their function is simply to act as homeostatic factors. There is little evidence in favor of James' idea that the effects produced by visceral feedback are responsible for emotional feelings.
James-Lange theory
Perception> Motor Reaction> Visceral Reaction> Emotion
Cannon-Bart theory
Perception> Thalamic reaction> Emotional sensation
Body Changes James had pointed out that for each emotion there was a specific pattern of visceral response. Ax (1953) conducted an experiment. It exposed the subjects to a situation designed to provoke either fear or anger. He measured a series of physiological response patterns to these two situations.
The two situations produced activity in the sympathetic nervous system, with significant differences appearing in various visceral indicators. Differences in visceral patterns were calculated by averaging the results of the subjects in each group, rather than comparing each subject to himself.
The dependent variables that are used to measure emotions are fundamentally of three types. The questionnaires and self-reports. People answer questions related to their feelings and emotions. They are a way of collecting information about the subjective experience of the individual himself that tries to bring internal states to his consciousness.
They must be reliable and valid. Reliability refers to consistency over time. Validity refers to these instruments measuring what they claim to measure. The use of behavioral measures. They have been preferred from the behavioral approaches to the study of emotion. Measures of motor behaviors that can be observed externally. The first refers to the measure of emotionality, generally in the open field. The animal is usually put in a new space for him.
This situation usually causes fear in the animal. Other measures that have been used are related to the experimental study of frustration, both in animals and in children. The frustration response occurs when an obstacle prevents you from achieving a goal that can satisfy a need. Frustration increases aggression, just as the existence of aggression indicates that there has been frustration. Physiological variables. Record body changes through a series of peripheral physiological measures such as respiration, heart rate, skin conductance. Behavioral measures may consist of the typical description of the behavior by the experimenter. Other more sophisticated techniques are the active and passive avoidance techniques used in the study of the conditioned emotion paradigm. The most widely used psychophysiological measures are:
- The galvanic response of the skin. The resistance of the skin to the flow of electrical current. This measurement constantly fluctuates. When a new stimulation occurs, changes in the galvanic response occur.
- Blood circulation. The most commonly used measurements are blood pressure and blood pulse rate.
- Respiration rate. It is one of the most frequently used physiological measures in the study of emotions.
Until now it has been possible to differentiate the intensity of a certain state of arousal, but it has not yet been possible to show the existence of different patterns of activity related to different emotions. Other measures involve stimulating different parts of the brain. The variables that are recorded are central physiological measures. Stimulation can be electrical or chemical. There are various structures involved in emotional behavior, such as the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the reticular formation, the limbic system.
Facial expression.
For some these expressions are universal, while for others they depend on culture. In the Ekman and Friesen experiments, subjects were shown photographs of different facial expressions to observers of different cultures and asked them to indicate which of the emotions that were presented in a list corresponded to the expression shown in each Photography.
Five different cultures agreed by assigning an emotion to each of the five faces shown in the photographs. It was concluded that facial expressions were universal.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.


