Attention is a quality that is part of our basic psychological processes, among them we also find memory, emotion, motivation, thought... For each type of process, there are several theoretical models that attempt to explain both the origin and the procedure of each mental function. In this case, the objective of the attentional models is to analyze how our mind acts when something awakens our attention and maintains that state for a prolonged period of time.
The kind of rigid Broadbent filter and the model of Treisman attenuated filter They were two great theories thanks to which we can conceive new studies and theoretical proposals about attention. In the following Psychology-Online article: rigid and attenuated filter model. We will talk about the experiments and theories of Broadbent and Treisman.
Index
- Broadbent Rigid Filter Model
- Divided memory breadth paradigm
- Treisman Attenuated Filter Model
- Other attentional models
Broadbent Rigid Filter Model.
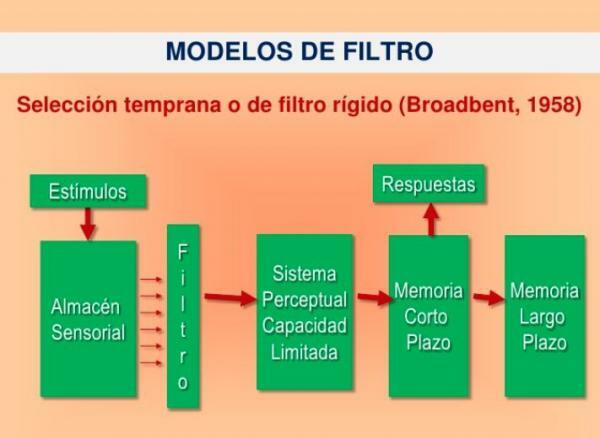
The rigid filter model is part of the attentional models and resorts to the bottleneck analogy. That is, it postulates the existence of a filter that regulates the entry of the inputs. To conduct attention experiments that demonstrate both filter models, subjects receive two verbal messages at the same time, one in each ear and they only have to attend to one of them (dichotic listening).
The attended message is remembered, while the unanswered message is not. Hence, these models postulate the existence of a filter that selects only one of the two messages.
What is the rigid filter model
Broadbent's rigid filter model is related to the so-called multistore theory. This divides the memory into three main structures:
- Sensory
- Short term memory
- Long term memory
This model considers that attention selects information before it is given meaning. For this reason, this model is also called early care model.
Broadbent's experiments consist of presenting the subject simultaneously 2 verbal messages dichotically, that is, a different sound in each ear, the subject attends to one of them and then is able to remember it, but the unattended message is not remembered.
Variants of the Broadbent model
Cherry (1953) developed an experimental variant that consisted of introducing variations in the irrelevant message. These variations consisted of the following: the irrelevant message it began in one language and ended in another. the irrelevant message it began with a male voice and ended with a female voice. the irrelevant message was interrupted by an auditory signal ...
When asking the subjects about the irrelevant message, they did not remember the content or the language, but in some cases they noticed the change of voice or signal auditory, which implies that the irrelevant message receives elementary processing, at least in its physical features but not in its properties semantic.
Divided memory breadth paradigm.
An experimental paradigm developed by Broadbent (1954) known as the divided memory width technique informs us that when a verbal message is presented simultaneously and dichotically (for example: digits) subjects remembered both messages, but not in their actual order of presentation, but grouped by channels.
Only when the presentation speed becomes very slow (one item every 2 seconds) do subjects remember the items in their actual presentation order.
Example of the paradigm
- Left ear: a, s, d.
- Right Ear: q, w, e.
- The order of presentation was: a, q, s, w, d, e.
- The subject remembers: a, s, d, q, w, e or q, w, e, a, s, d.
- He does not remember it according to the actual order of presentation, but grouped by channels.
The Basic Principles of Broadbent's Rigid Filter Model
- The subject receives many sensory messages from the environment, these will be processed in parallel, at the same time, and are temporarily retained in the sensory memory.
- But as according to Broadbent, we can only process one message at a time to avoid the central channel overload there a filter that chooses which message will pass to the central channel.
The rest of the information is lost. But what does it depend on whether a message is selected? According to this author, it will depend on the properties of the stimulus and the needs of the organism. The model proposed by Broadbent it is called a rigid filter because it proposes that the filter is an all-or-nothing device that only focuses on one message at a time.
Treisman Attenuated Filter Model.
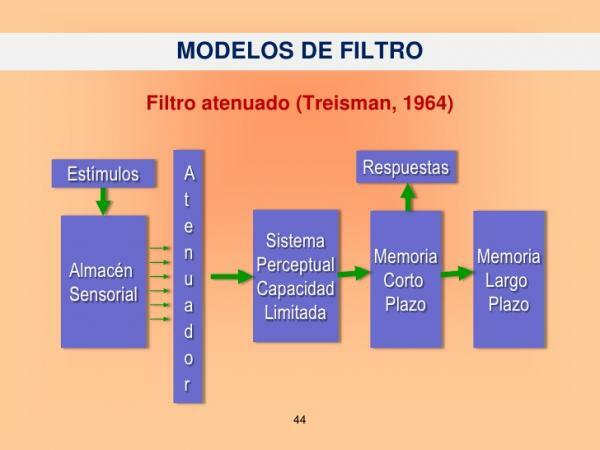
Treisman conducted experiments whose results indicated that the filter is not all-or-nothing, as stated by Broadbent, since it allows the irrelevant message to be analyzed, at least in those cases where it is discriminable in relation to the main message.
Treisman (1969) proposes that the filter is an attenuation mechanism for all messages. The relevant message passes the filter while the others - irrelevant - are attenuated so as not to overload the central processing mechanism.
Treisman's attenuated filter model demonstrated that additional tasks were not completely ignored, which He suggested that the attention did not have a rigid filter, rather it had a mechanism that attenuated the messages not catered.
Comparison between the Treisman model and the Broadbent rigid filter
The model proposed by Treisman is similar to Broadbent's, the fundamental difference is how the filter works, is different since for Treisman the filter attenuates the irrelevant messages, and the irrelevant message receives some analysis. The grayed out messages receive some kind of analysis, this follows the fact that if it is detected some salient feature in one of the unattended channels, our attention will be diverted to said message.

Other attentional models.
Although the attentional models that we have mentioned are the best known, over the years and after several investigations, a series of theories have been developed that e
Deutsch and Deutsch late filter model
They decided to propose the first model of late or post-category filter. According to this model, all external stimuli are stored in sensory memory and, based on this, the stimuli are processed and analyzed using an analyzer system.
Kahneman model
This model proposes that attention is a finite and limited resource that can be distributed to carry out one or more activities. This distribution will be based on three factors:
- The difficulty of the task
- Intrinsic or personal motivation
- The activation level o arousal
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Rigid and Attenuated Filter Model, we recommend that you enter our category of Basic psychology.


