Melatonin is a hormone produced in the pineal gland (located in the brain) that helps us to regulate sleep already strengthen our immune system. Recently, certain beneficial effects have been discovered that have led to the production of some melatonin-dosed medications, which can be purchased at pharmacies and others establishments. However, before buy melatonin, it is important to know what it does, what its benefits are and what dose it is advisable to take.
The two situations in which melatonin should be taken should be highlighted. The first is that situation associated with a specific problem due to stress and / or anxiety, and the second is that associated with people with early awakenings and / or nocturnal awakenings during the sleep cycle. The Vitae laboratory presents its formula CalmTu Night based melatonin Y magnesium, in addition to other natural plants such as valerian, california poppy, passionflower Y balm that helps to reduce the time to fall asleep, improve its quality and help you rest while you sleep
In this Psychology-Online article, we will talk about melatonin for sleep: dosage, contraindications and that food they contain it.
Index
- What is melatonin?
- What is melatonin good for?
- How to take melatonin to sleep
- Melatonin pills
- Melatonin foods
What is melatonin?
Is hormone is produced by Pineal gland and its main function is regulate our sleep cycle and wake up. Melatonin is produced regularly in a 24-hour cycle, this cycle has a release peak where it is produces more melatonin and, thanks to this, our biological clock - or circadian rhythm - synchronizes and follows its cycle.
This hormone was discovered more than 50 years ago, however, it has begun to be marketed as a natural sleeping pill massively since 2005, approximately.
If you are looking for advice on how to fall asleep, it is very possible that you will come across information related to melatonin and formulas that contain this hormone. While it is true that there are numerous studies that claim that melatonin helps regulate sleep, many of them end up concluding that it is more beneficial to find other ways to treat insomnia[1].
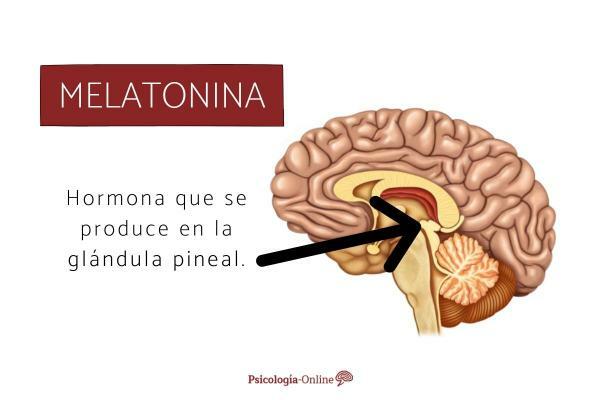
What is melatonin good for?
Melatonin plays a very important role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Maintaining a good balance of melatonin and cortisol is essential to stay awake during the day and to be able to sleep well at night.
How does melatonin work?
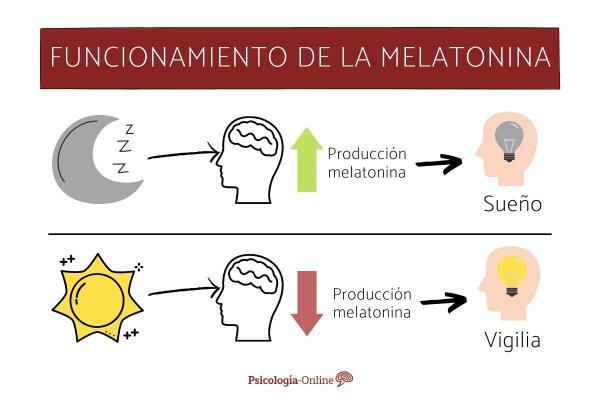
When it gets dark and it starts to get dark, darkness stimulates the pineal gland. Stimulation of the pineal gland causes melatonin to be produced. Melatonin, in turn, encourages sleep.
When it is daytime, the process occurs in reverse. When the retina perceives light, the production of melatonin stops and the level of the hormone decreases, causing sleep to disappear and wakefulness appears. This is how we wake up.
Melatonin benefits
As we have commented previously, one of the basic functions of melatonin is to regulate our circadian rhythm and as a consequence helps us fall asleep in case it costs us. Research suggests that melatonin pills can help treat sleep disorderssuch as delayed sleep and insomnia. By the properties of melatonin, we can see that it has various benefits.
The problem with these formulas is that their effects are mild in a healthy population (people without anxiety or ADHD). Medical studies reveal that people who take these supplements sleep an average of 10 minutes longer, so these natural sleeping pills are not as effective either. Even so, they have shown to have more beneficial effects in the following aspects:
- The ADHD treatment.
- The prevention of jet lag.
- Relief of the symptoms of winter depression.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- The prevention of aging by having an antioxidant effect on cells.
- The slowing of aging.
- Neuroprotection: Melatonin is a neuroprotector.
Here is a simplified outline of how melatonin works and what it is for.
How to take melatonin to sleep.
Thanks to the recent fame that melatonin has acquired, today it is very easy to buy it in a pharmacy and even in certain supermarkets at a fairly cheap price. Next, we will see how melatonin is taken.
- According to many experts, before taking melatonin pills, it is important to see a doctor so that it regulates the dose we should take.
- Where should melatonin be bought, at the supermarket or at the pharmacy? This is another fairly common question. Although it is true that the product and the active ingredient are the same, it is recommended go to a pharmacy (and even the doctor as we have mentioned) so that they advise us correctly in the event that we want to take melatonin.
- It comes in pill form and, if you want to know how to take melatonin to sleep, the first thing to keep in mind is that it should be drink regularly.
- To fall asleep, it must be taken in advance, that is, between one hour and 30 minutes before going to bed.
Melatonin in pills.
In addition to knowing what it is and what it is for, you should know the recommended melatonin doses, its contraindications and side effects.
Dose
How many milligrams (mg) of melatonin must be taken to be effective? The optimal dose of melatonin is unclear.
Studies have been conducted with doses of 2 mg, 3 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg and significant benefits have been found from the 2 mg dose of melatonin. Being the 10 mg maximum adult melatonin dose. Therefore, it is not recommended to exceed 10 mg (5 tablets of 2 mg).
Contraindications of melatonin
In principle, taking melatonin is safe in the short term. Unlike most sleep drugs, melatonin does not cause dependency or habituation.
Taking melatonin is contraindicated if some medications are followed as it can interact with these drugs:
- Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents.
- Anticonvulsants.
- Contraceptives
- Drugs for diabetes.
- Immunosuppressive drugs.
If you are being treated with any of these medications, you should consult a professional before taking melatonin.
It is advisable not to take these supplements in peak hours sunlight. Melatonin is also not recommended during pregnancy nor during lactation. Finally, can people take melatonin? kids? No, melatonin is not recommended for infants.
Does melatonin make you fat? It seems quite the opposite. By regulating our biological rhythm, melatonin helps us burn calories and is able to prevent overweight and obesity[2]. According to a study by the University of Granada[3], consuming melatonin helps you burn more calories and stop gaining weight. Researchers in this 2018 study found that the hormone has an anti-obesity mechanism, as it has very potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-obesity effects.
Side effects of melatonin
However, melatonin can have some side effects such as:
- Headache.
- Dizziness
- Sickness.
- Drowsiness.
- Depressive symptoms
- Mild tremors
- Mild anxiety
- Colic.
- Irritability.
- Reduced alertness.
- Confusion.
- Disorientation.
Melatonin foods.
If you want to get the benefits of melatonin without taking pills, you can help your body by consuming some of the foods that contain melatonin:
- Rice. One of the foods richest in melatonin is rice.
- Oatmeal. Oatmeal is another of the foods with melatonin.
- Corn. Along with oats and rice, corn is one of the foods that contains the most melatonin per gram.
- Tomato. This fruit helps to fall asleep.
- Banana. It also helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
- Walnuts. Each gram of walnuts contains 3.5 nanograms of melatonin.
- Cherries. Those that contain the most melatonin are the most acidic in taste.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Melatonin for sleep: dosage, contraindications and foods, we recommend that you enter our category of Psychopharmaceuticals.
References
- Pérez Collado, E. M., Quesada Martínez, M. I., & Parra Parra, Y. (2015). Melatonin: A Healthy Alternative To Fight Insomnia?
- Prunet-Marcassus, B., Desbazeille, M., Bros, A., Louche, K., Delagrange, P., Renard, P.,... & Pénicaud, L. (2003). Melatonin reduces body weight gain in Sprague Dawley rats with diet-induced obesity. Endocrinologistand, 144 (12), 5347-5352.
- Fernández Vázquez, G., Reiter, R. J., & Agil, A. (2018). Melatonin increases brown adipose tissue mass and function in Zücker diabetic fatty rats: implications for obesity control. Journal of pineal research, 64 (4), e12472.
Bibliography
- Benítez-King, G. (2012). Melatonin: a flash of life in the dark. Fund of Economic Culture.
- Illnait-Ferrer, J. (2012). Melatonin: topicality of a forgotten hormone. CENIC Magazine. Biological Sciences, 43(3).


