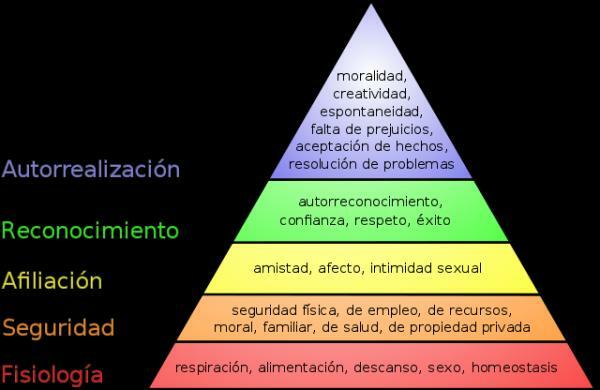
Abraham Maslow is one of the leading representatives of humanistic psychology. Maslow's theory of needs provides an analysis around the factors that influence the development, motivation and personal fulfillment of a human being. It consists of a pyramid that ranks human needs. His theory acquires very visual information when it is structured in the image of a pyramid that contains five different sections that we describe in this article in Psychology-Online. These are the five main points of the Maslow's Theory of Needs.
Index
- Physiological needs
- Security needs
- Affiliation need
- Recognition needs
- Self-realization
1. Physiological needs.
Right at the base of this Maslow pyramid are those aspects of first necessity in relation to the life and well-being of a human being. From this satisfaction of physiological needs, the human being can advance in the direction of self-realization reaching other purposes that are at the different levels of this picture. In this group of basic needs are grouped, for example,
2. Security needs.
In the next section of this pyramid are those needs that are aligned with this objective. The second step corresponds to the need for protection, security and stability. By means of this positioning before reality, once the basic needs are covered, the human being seeks the roots of a security from which to make decisions that transcend immediately and connect with a life project based on the short or long term.
For example, searching for a economic security through a job that provides a monthly income. Home it is also a manifestation of that longing for security through the well-being of one's own space. In relation to this point, this is one of the reasons why uncertainty and concern Long-term unemployment or job instability can cause so much suffering by jeopardizing the satisfaction of this important need.
3. Affiliation need.
At the third rung of Maslow's pyramid of needs is the need for love, affection, and group membership. The social dimension of the human being is revealed through the links that people establish with each other by building new stories. Social ties that provide a rooted in the group and experiences that add meaning to the present through of love, trust, friendship, affection and company facing loneliness.
Through this encounter with others, the person transcends their own individual reality by establishing social connections with others. These bonds with others are an important source of happiness. Furthermore, a human being also knows himself through the time that he shares with others. From this need lies the importance of social skills.
4. Recognition needs.
In the next section of Maslow's pyramid, which describes one of the best-known motivational theories, we find those needs that are linked to the self-esteem of a human being. The social needs described in the previous section connect with this new purpose that leads to the value of the environment.
This recognition can not only express the unconditional admiration that a person feels towards someone to professional level, but also, of the own vision that a human being has of himself and the valuation, is tell, self-concept and self-esteem. Social ties are important and valuable, but so is the bond that a person maintains with himself. This reality also reflects the social dimension of the human being, and in turn, his individual being.
5. Self-realization.
The top of Maslow's pyramid leads to that call for self-realization through the search for a happiness to which the human being reaches when he has covered the needs described in the previous points. This step corresponds to development of potential and personal growth. In this section of self-realization, there is also the personal and social development, spirituality and personal search.
All the sections of this pyramid are important and have their own meaning, within an aligned hierarchy with the human being, since in addition, this look of self-realization has a comprehensive approach to needs. It is not possible to get to this point in the pyramid without having basic needs covered.
Every human being who reaches this state of Maslow's pyramid writes his own story of self-realization through decision-making, freedom, search for meaning, the development of a mission, the practice of personal values and the achievement of goals.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Maslow's Theory of Needs, we recommend that you enter our category of Personal growth and self-help.
Bibliography
- Angarita, J. R. (2007). Maslow's Theory of Needs. Obtained from Maslow's Theory of Needs: http://doctorado. josequintero. Net / documents / Teoria_Maslow_Jose_Quintero. pdf.


