Many patients who suffer from anxiety attacks feel that they will also end up suffering a heart attack. The truth is that the symptoms of both pictures can be very similar and can therefore be easily confused. We must bear in mind that the symptoms of a heart attack can be very variable between patients, making its detection more complex and causing even more confusion between the distinction between anxiety and heart attack.
Despite their similar symptoms, the truth is that both pictures are completely different in terms of their causes and consequences. Do you know the difference between an anxiety attack and a heart attack? To delve into this matter, continue reading this Psychology-Online article in which we expose some differences between anxiety and heart attack. We explain everything you need to know to differentiate a heart attack from an anxiety attack.
Index
- Anxiety, panic attack, and heart attack
- Physical symptoms of anxiety
- How to distinguish an anxiety attack from a heart attack: 7 differences
Anxiety, panic attack, and heart attack.
The American Psychiatric Association's Dictionary of Psychology defines anxiety as a emotion characterized by apprehension and somatic symptoms of tension. On a more cognitive level, it includes the anticipation of imminent danger, catastrophe, or misfortune, which is why the body prepares to deal with that threat.
Although a Anxiety Attack (understood as an acute manifestation of its symptoms) can appear in different pictures, the panic disorder it is one of the pictures in which anxiety symptoms at the physiological level are more representative. In this article we talk about types of anxiety and their symptoms.
On the other hand, when we talk about heart attack, we usually refer to myocardial infarction. For this reason and the aforementioned, in this article we will refer specifically to panic attacks when Let's talk about anxiety attacks and when we talk about heart attack we will be referring to myocardial infarction specifically.
Physical symptoms of anxiety.
Because the physiological symptomatology of anxiety is precisely what we can confuse with the symptoms of a heart attack, it is the one that we focus on in this section. As we have already mentioned, we will focus on the symptoms of panic disorder, the symptoms of which include:
- Sweating
- Shaking.
- Choking sensation and shortness of breath.
- Pain or discomfort in the chest.
- Palpitations or changes in heart rate.
- Nausea or abdominal discomfort.
- Chills or feeling hot
- Numbness or tingling sensation.
- Derealization
- Fear of losing control and fear of dying.
The symptoms that make up this picture lead patients to have the feeling that they will end up having a heart attack. However, if we look at the definition of the American Psychiatric Association set out above, anxiety is a response that, although excessive, prepares the body to face a threat imminent. After a while, the anxiety response will begin to decline. Therefore, an anxiety attack does not cause a heart attack and neither does death. In this article we talk about fear of heart attack.
Now, far from the physical damage that could be associated, the danger posed by high physiological activation or anxiety attacks are more associated with the psychological dimension: associating situations with said activation disproportionate. This causes problems and / or anxiety disorders.
How to distinguish an anxiety attack from a heart attack: 7 differences.
How do you know if it is a heart attack or an anxiety attack? Here we will see what it feels like to have an anxiety attack and how to differentiate it from a heart attack:
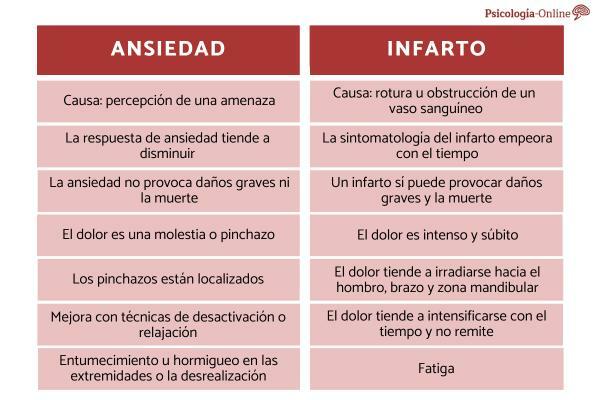
Difference in its causality
Although this difference will not help us especially to distinguish one from the other when we notice the symptoms, the truth is that it is the most relevant difference.
As we have pointed out, anxiety consists of a highly arousal response to the perception of an imminent threat. The body prepares to face this threat.
It has nothing to do with heart attack, which occurs when blood flow decreases mainly due to a blood vessel rupture or obstruction.
Difference in its temporality
Preparing the body to deal with threats involves significant energy expenditure. After a period of time, the anxiety response tends to decrease.
On the contrary, an obstruction of the blood vessels or a rupture of these will cause lesions that do not tend to remit over time, but quite the opposite. The consequences will be worse the longer blood flow is interrupted.
Difference in its consequences
As we already anticipated, a heart attack can cause serious problems due to the lack of blood supply, even leading to death.
The consequences of an anxiety attack do not usually involve physical damage, although the appearance Recurrent of such attacks can cause, over time, damage to the system vascular. As we have pointed out previously, the consequences of anxiety attacks are usually more related to the psychological field.
Differences in their symptoms
Taking into account that the symptoms of both conditions are very similar, there are some differences that can help us distinguish an anxiety attack from a heart attack:
- The pain: The predominant symptom of myocardial infarction is pain, a sudden intense pain in the center of the chest that radiates to other parts. On the contrary, if discomfort or pain appears in an anxiety attack, it is usually not so serious and is limited to the sensation of pricking.
- The location of the pain: the pinpricks of anxiety attacks are perfectly specific and localizable. In contrast, heart attack pain typically tends to radiate to the shoulder, left arm, left mandibular area, and even the central back area.
- Evolution and improvement: anxiety symptoms improve when the person applies deactivation or relaxation techniques. This does not happen in cases of heart attack in which the pain tends to intensify over time and does not subside even with postural changes.
- Characteristic symptomsFinally, there are symptoms that seem more characteristic of a heart attack, such as fatigue even in situations of rest; and others more characteristic of the anxiety attack, such as numbness or tingling in the extremities or derealization.
Knowing the difference between angina and anxiety you will be able to distinguish between the two episodes. When in doubt, it is best to go to the emergency medical service.
Finally, in this article you will find what to do before an anxiety attack.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Differences between anxiety and heart attack, we recommend that you enter our category of Clinical psychology.
Bibliography
- American Psychiatric Association (2020). APA Dictionary of Psychology. Recovered from https://dictionary.apa.org
- American Psychiatric Association (2014). DSM-5. Reference guide to the diagnostic criteria of the DSM-5-Breviary. Madrid: Editorial Médica Panamericana.
- García-Palacios, A., Botella, C., Osma, J. and Baños, R.M. (2014). Panic disorder and agoraphobia. In Caballo, V.E., Salazar, I.C. And Carrobles, J.A. (2014) Manual of Psychopathology and Psychological Disorders. Madrid. Pyramid.


