Have you ever wondered how the brain is made? Have you ever been curious to know how we understand the information that comes from our environment? Why do people have brain injuries? What has happened to him? These are questions that many people ask themselves according to different situations that they go through throughout their lives. There are those who live their lives without major health complications, but there are people who have certain areas of the brain affected and, in this way, their daily activities are diminished.
Having knowledge about this topic can help us answer many questions that are presented to us. Perhaps you have experienced a difficult moment and this had an impact on you, or you have probably been in contact with someone who has these problems. Do you want to know more about this? In this Psychology-Online article we will provide you with information about the white matter of the brain, its definition, structure, functions and lesions.
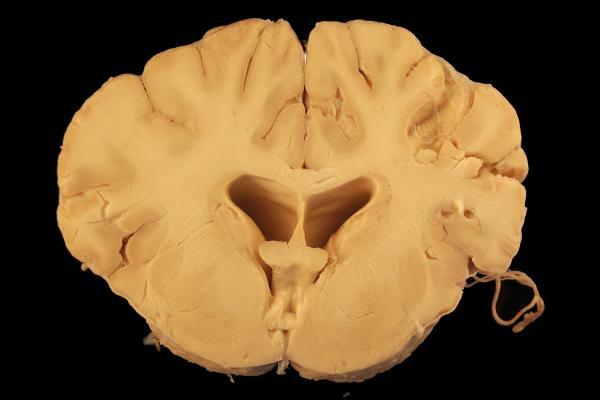
When we talk about the white matter of the brain, we refer to
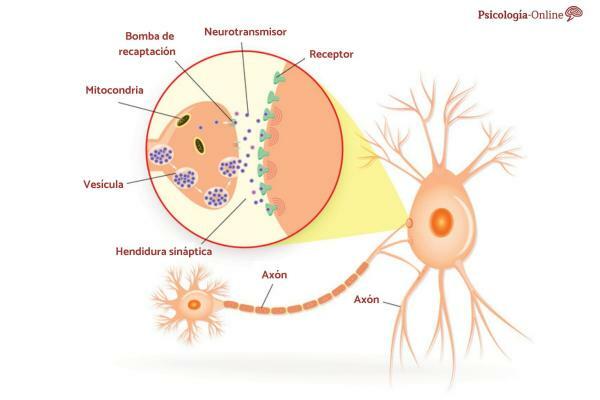
In order to understand even more about the white matter of the brain, it is important to know its structure. To begin with, we will say that the white matter of the brain possesses neurons that are lined with a white coating called the myelin sheath. This substance's main function is to accelerate the transmission of information between neurons through electrical signals. The presence of neurons within the white matter of the brain is crucial since they are the responsible for receiving information from other sectors of the body and transmitting it to other neurons. In other words, without the existence of neurons, it would not be possible for us to have the ability to perform various cognitive and motor activities in our daily lives.
At the same time, These neurons have structures called glial cells inside them. that provide valuable support. The role of glial cells in the composition of neurons is to maintain the structure of neurons so that they can have the ability to send electrical impulses to other neurons.
The white matter of the brain it is located mainly in the internal areas of the central nervous system as well as in certain areas of the spinal cord.
For more information on each of these parts, you can consult the following articles:
- Neuron.
- Glial cells: what are they, types and functions.
- Central Nervous System
Given the importance that the white matter of the brain represents, there are aspects that we can consider as relevant when it comes to understanding its operation.
- On the one hand, this substance has as its primary function guarantee the correct transmission of information through the connections established between neurons that are part of the human body.
- As for other functions performed by the white matter of the brain, we will mention that it is also found related to the area of thought, memory, learning new content, intelligence, among others. This is transcendental since without the action of neurons, these sectors in people's lives are affected.
- Its correct operation has a clear impact on the development of activities that require concentration and attention.
When the information processing speed is not correct due to slow connections between neurons, inconveniences arise that translate into difficulties that a person may have in their life everyday. For this reason, the presence of brain lesions is directly related to different neurological disorders. In other words, when there are complications in the white matter of the brain, characteristic symptoms appear linked to damage to the cerebral cortex. Next, we will mention the most relevant ones that must be taken into account:
- Lack of motor coordination (Difficulty in performing body movements)
- Short-term and long-term memory loss
- Feeling of physical exhaustion
- Blurry vision
- Lack of muscle strength
- Difficulties in concentration and attention
The presence of any of these symptoms can be a indicator of diseases such as Alzheimer's, dyslexia, attention deficit disorder, dementia, multiple sclerosis, among others. Although these pathologies are usually more frequent in people over 60 years of age who suffer hypertension, this does not imply that we are facing a lesion in the white matter of the brain.
It is essential that the diagnosis be carried out by a health professional since he will be in charge of evaluating the characteristics of the patient such as age, sex, pre-existing and current diseases, family history, among others. In this way, this will make it possible to indicate an appropriate treatment to the needs of each person.
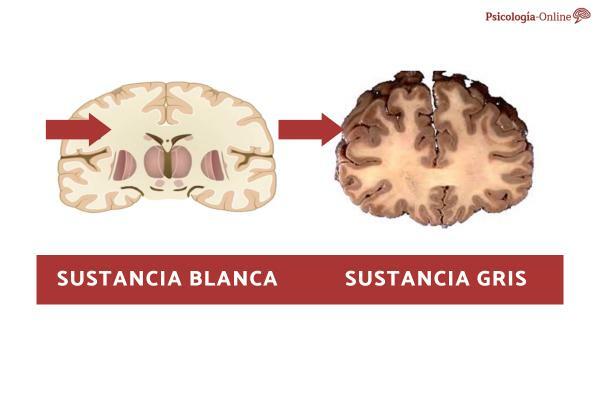
In this article, you can see what is the difference between the gray matter and the white matter of the brain.

This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to White matter of the brain: definition, structure, functions and lesions, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.



1 from 3
White matter of the brain: definition, structure, functions and lesions