The human brain is made up of different structures connected to each other and in turn made up of other smaller subdivisions. small that, through the connections between them, give rise to the basic psychological processes and the most important functions. complex. These functions help us function on a day-to-day basis, as they give us the ability to memorize, speaking and writing, as well as intervene in the processes of attention, perception, learning and thought.
Currently there are structures whose exact functions and their real involvement in the brain are unknown, so that we must continue exploring to continue discovering new structures, or to know in greater detail the already discovered. The mammillary bodies, which you may not have heard of before, are one part of this complex network. that we have in our head and is involved in some of the processes that we carry out continuously. Do you want to know where they are? What exactly are they and what do they do? In this Psychology-Online article we will talk about the Mamillary bodies: what they are, location and functions.
Index
- What are mammillary bodies
- Location of the mammillary bodies
- What are the mammillary bodies
- Functions of the mammillary bodies
What are the mammillary bodies.
The mammillary bodies are one of the parts that make up the Papez circuit. This set of nerve structures works through two circuits, efferent and afferent. Let's see how they work:
- The mammillary bodies send outputs through the mammillothalamic bundle to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus.
- The anterior nuclei of the thalamus, in turn, connect with certain divisions of the cerebral cortex.
- The cerebral cortex sends projections to the hippocampal formation back through the entorhinal area.
- At the level of afferences, the hypothalamus sends half of its projections, through the fornix, to the mammillary bodies; also receiving input from the medial prefrontal cortex.
In addition, it should be noted that the mammillary bodies are anatomically related to brainstem structures, with the septal nuclei, other hypothalamic nuclei, and with the nucleus of Broca's diagonal band.
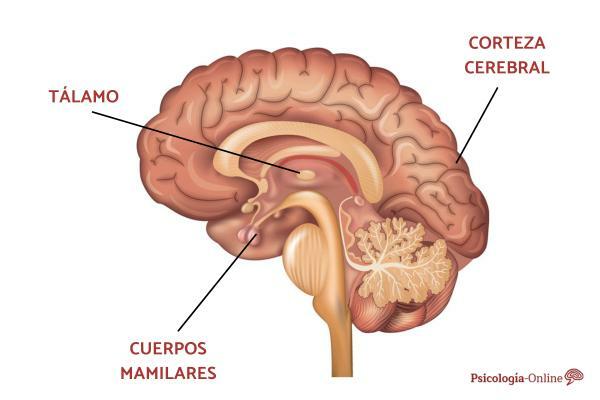
Location of the mammillary bodies.
The mammillary bodies are located in the limbic system. Next, we detail the structures that we must identify to locate the mammillary bodies:
- In the forebrain, we have the diencephalon.
- In the most ventral part of the diencephalon we find the hypothalamus, specifically in the anterior part of the thalamus, forming the floor of the third ventricle.
- Within this structure, we find several nuclei and fibers, as part of the gray matter of the brain, which we call mammillary bodies.
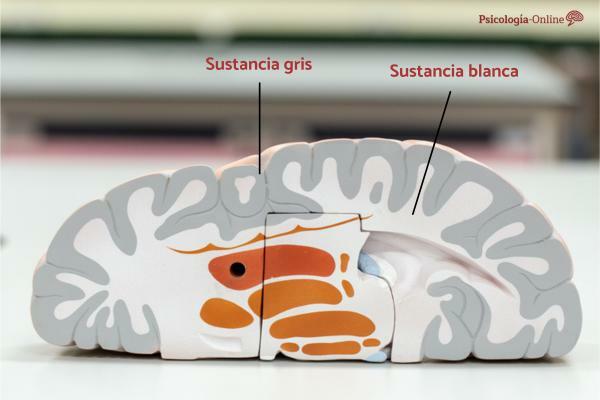
What are the mammillary bodies.
If you wonder how many mammillary bodies there are, you should know that it is a complex located in the brain and is made up of 3 nuclei mainly. The name of these nuclei of this hypothalamic region are:
- medial mammillary nucleus: constitutes the mammillary bodies, together with the lateral mammillary nucleus.
- lateral mammillary nucleus: constitutes the mammillary bodies, together with the medial mammillary nucleus.
- supramammillary nucleus (located dorsal to the two anterior nuclei): studies show its importance in the execution of spatial tasks and declarative memory. He is the one with the most information and who knows that he can modulate hippocampal function in two different ways: supramamillary-hippocampal pathway and supramamillary-medial septum pathway.
Various studies show the connections of the mammillary and supramammillary bodies with the hippocampus, both directly and indirectly, through the septal area. Despite this information, more studies are required to determine what their most outstanding characteristics are and if they are involved in other neuronal processes.
Functions of the mammillary bodies.
Little is currently known about the specific functions of the mammillary bodies. As part of the hypothalamus, the main functions of the mammillary bodies that are known are:
- principall control center of the vegetative nervous system and the endocrine system.
- control motivated behavior such as food and water intake, sexual behavior, etc. Thus, they are key in the control of homeostasis.
- Coordinate physical responses linked to emotional changes. Today's studies show the connection of the connections of those areas involved with emotion and memory, that is, with the thalamus.
Despite this, his involvement in memory processes is reflected in the appearance of brain alterations such as Korsakoff's syndrome, a diencephalic amnesia that occurs due to an affectation of the mammillary bodies of the hypothalamus and the dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus, as a consequence of a thiamine deficiency.
The most well-known aspect of the mammillary bodies are the pathways with which they connect. We know that are part of, at least, four brain circuits involved in different functions, such as memory. Specifically, some studies have shown its involvement in spatial memory.
What happens if the mammillary bodies are injured?
Clinical studies carried out in humans, by means of neuroimaging techniques, show that the alteration morphological circumscribed to the mammillary bodies, due to different pathological processes, is sufficient to induce severe and persistent impairments in declarative memory. Specifically, they show that these alterations are related to the inability of individuals to form new memories, of variable duration, from the moment of injury.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Mamillary bodies: what they are, location and functions, we recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Aranda, L., (2016). Implication of the mammillary region in spatial learning. Mexican Journal of Psychology, 33(1), 41-49.
- Carlson, N. R. (2014). physiology of behavior. Madrid. Pearson Education, S.A.
- Portell, I. (2015). diencephalon Autonomous University of Barcelona.
- Santin, L. J., Rubio, S., Cimadevila, J. M., Begega, A., & Arias, J. L., (1997). Spatial memory and mammillary bodies. Psychology writings. 1 (1), 70-81.


