Observing things around us, we tend to integrate the different parts of visual stimuli and organize them into meaningful ways. In general, we carry out this perceptual elaboration of stimuli in a totally unconscious way, so it seems to us that we perceive things in this way simply because "they are like that".
This impression of adherence of the percept to objective reality is usually quite correct. but sometimes perception misleads us as perceptual configurations are created illusory. Thenwhat are perceptual illusions? In this Psychology-Online article we are going to see its causes, the different types and some examples.
Index
- What are perceptual illusions
- Causes of perceptual illusions
- Types of perceptual illusions and examples
- Differences between perceptual illusions and hallucinations
- Examples of perceptual illusions
What are perceptual illusions.
Perceptual illusions represent, unlike perceptual constancy, an inaccurate perception of real objects
It can be said that the perceptive illusions They are not only optical illusions, since the latter is based on the introduction of visual tricks that work with human perception; while perceptive illusions are rather a cognitive phenomenon whose protagonist is the cerebral processing of sensory information.

Causes of perceptive illusions.
The phenomena of perceptual illusions are unequivocal examples of a general truth: perception is organized and cannot be regarded simply as "given" by the impression of external events. In this way, perceptive illusions are produced by a series of influences:
- biological influences: our nature of attention is selective and, in addition, we see images as perceptual sets (we fill in the spaces of the image to complete it).
- psychological influences: Perceptive illusions are the product of the emotional context and the schemes learned throughout our lives.
- Sociocultural influences: are those that integrate cultural assumptions and expectations, as well as the effects of the physical context.
Types of perceptive illusions and examples.
To better understand what perceptual illusions are, it will help you to read the following examples on the matter:
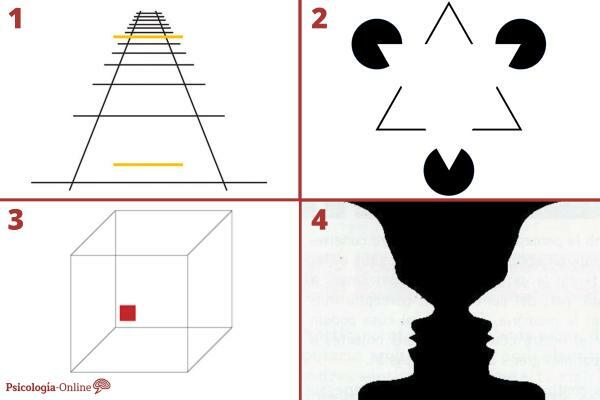
1. ponzo illusion
depth perception it can be altered by drawing two divergent straight lines on the sheet. If identical elements are added to the drawing, but appropriately spaced apart, the objects that are in the convergence of the lines appear further apart and therefore higher than those found where the lines diverge more.
2. the illusion ofe Kanizsa
Three colored disks placed on the same plane and of which a small portion has been cut out give the illusion that a white triangle is also drawn on the sheet. There is actually no triangle, as happens when changing the layout of the floppy disks: our mind completes the picture with just the details.
3. Necker's cube
What is the front face of the cube? And the back? The brain can't decide why has no landmarks to determine which part of the cube is closer and which is further away.
4. Illusions related to color
On Rubin's cup both the object (the cup) and two human profiles can be distinguished depending on whether one pays more attention to the white of the cup or the black of the background.
Another deception in the perception of color is the one that occurs when a homogeneous band of color is superimposed on a blurred background: the end of the stripe that is in the darkest part of the background will appear lighter and vice versa.
5. the impossible figures
There are objects that can only live on paper, but they are totally unrealizable. An example is the endless staircase, in which you can go down or up to infinity because the first and last steps coincide. Endless stairs and other impossible objects are also frequently found in many works by Maurits Cornelis Escher.
6. ambiguous images
Young or old? In "My Wife and my mother-in-law", a caricature made by the English artist W.E. Hill in 1915, you can see both a three-quarter length shot of a young woman and a pensive old woman in profile.
Differences between perceptive illusions and hallucinations.
Perceptive illusions and hallucinations are phenomena in which an erroneous perception is made. However, unlike perceptual illusion, which misinterprets a really existing stimulus, the hallucination encounters an external stimulus that does not exist absolutely.
Some examples of hallucinations are: when a person hears a voice without there being a sound or, on the other hand, sees a person and object where there is really nothing or no one. Click on our title Types of hallucinations: causes and examples, if you want to know more about this topic.
Examples of perceptual illusions.
Other examples of perceptive illusions that occur regularly are:
the illusion of the moon
The moon appears smaller when it is at the zenith than when it is on the horizon. The explanation for this phenomenon is that The magnitude of an object is determined by comparing it with the environment.
In this way, when we see the moon on the horizon we compare it with elements of the landscape while that when it is at the zenith there are no reference points and for this reason it seems more little.
The contrast between black and white
Another situation of perceptive illusion can be easily verified by looking at certain floors with black and white marbles that represent a series of cubes seen of imbalance. At times it seems to us that the white faces are "closer" to us, as if protruding like an extended summit.
However, if we continue to observe, at some point the arrangement is reversed: the white parts are receding from us as if they were cavities and the dark parts appear to be protruding.
If you liked this article about perceptual illusions, we recommend you read our article Cognitive distortions: what they are, examples, types and exercises, which speaks of the erroneous interpretations about reality, which prevent us from experiencing the situations that occur to us objectively.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Perceptive illusions: what they are, causes, types and examples, we recommend that you enter our category of cognitive psychology.
Bibliography
- Burla, F., Capozzi, S., Lozupone, E. (2007). Elements of psychology, pedagogy, sociology for the health profession. Milan: Franco Angeli.
- Canestrari, R., Godino, A. (2002). Introduction to general psychology. Milan: Mondadori.
Perceptive illusions: what they are, causes, types and examples