The producer tax is another market distortion factor, being its affectation in the microeconomy object of study, although at first sight this tax seems a economic and tax policy more for the collection of resources that help the state to finance expenses public; these measures they have an impact on market equilibrium and income distribution.

Advertisements
Therefore, it affects all economic agents, not only the producer and the state, but also the consumer, thus altering the behavior of supply and demand.
The study, of this distortion factor, allows to provide the fire and the economic impact that is generates for economic agents and thus establish measures that help mitigate such effects.
Advertisements
In this article you will find:
What is the producer tax?
It is a tribute to tax lien that fall on the productive activities of companies, established by the tax laws and regulations in each country.
These producer taxes, like any other tax, represent contributions of a obligatory so that the productive sector of the country also contributes with the financing of the expenses of the state.
Advertisements
Types of producer tax
These taxes can be established through three modalities that are:
single payment tax
These taxes are established by paying a fixed amount corresponding to a certain period of time, which represent entry barriers for a certain market, limiting access to less economically efficient companies.
Advertisements
profit tax
This is a direct tax It is established on the benefit or profitability obtained by a company during a certain period, being progressive, therefore, the more the company earns, the more it pays, as is the Corporation Tax.
Tax on production and import
It is a tax contribution paid by companies for certain quantities produced or imported and based on these amounts is the value of the tax, such as taxes on the production of real estate assets.
Advertisements
Why are producer taxes established?
producer taxes are established for various reasons, among those the following:
The first reason the state taxes producers is to raise monetary resources to finance public spending, such as roads, health, education or others.
The second reason is to control and penalize the negative impact generated by the production processes of industrial companies in society and the environment, under the concept of whoever pollutes pays; In this way, it contributes to the economic system, encourages ecological and sustainable production and also helps finance the repair of the damage caused.
The third reason is to protect the national industry, establishing taxes such as tariffs on the import activities carried out by the companies, raising their costs and thus generating a competitive advantage for the production national.
What is producer surplus?
Producer surplus is the additional benefit or extra profit received by a producer from sales generated at a higher price than he would be willing to accept for said product or service; as a result of the behavior of the law of supply and demand that is generated in the free market.
Basically, producer surplus results from the difference between the price he receives for the sale of a good and the minimum price that he would be willing to accept for it, that difference would be his surplus as producer.
surplus, which it is negatively affected by interventionist measures such as taxes.
The producer tax and the welfare loss
When the state establishes producer taxes, these affect what is produced by increasing its price, which implies a loss of well-being; Therefore, this additional value produced by the tax prevents both producers and consumers from generating a profit.
This profit represents the surpluses of the producer and the consumer that together generate well-being, therefore, a reduction in the surpluses affects the degree of well-being.
Well, consumers will have to pay more and producers will charge less, since even when the tax falls on the producer, this will also affect the final sale price, therefore, the market contracts, discouraging economic exchanges between producers and consumers.
Effects of the tax on the producer in the short and long term
The producer tax, like any interventionist measure, generates distorting effects on market supply and demandboth in the short and long term.
Short term:
The first short-run effect is the increase in the supply price, since the companies will be motivated to increase the sale price to compensate the value of the loss caused by said tax in their profits.
This implies that consumers will have to pay more for the products or services offered, but producers' sales will decrease.
Long-term:
In the long run the supply curve becomes elastic, in this case taxes will reduce only consumer surplus and producers will not be affected by their surplus margin.
This is because long term producershave enough time to make adjustments to costs or other factors of production, in such a way that they can face or offset the impact of the tax.
Therefore, although the obligation to contribute this tax falls on the producer, in the long term the economic incidence of the tax is transferred to the consumer through the purchase price, thus affecting their income.
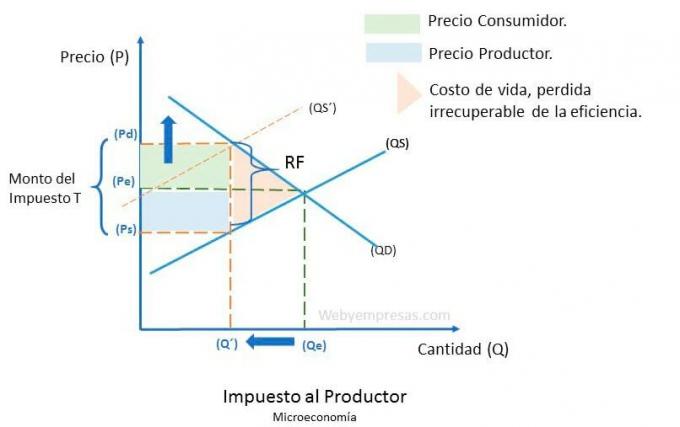
Graphic representation of the effect of the producer tax
producer's tax affects the supply curve, shifting it to the left, creating a new equilibrium in the market, plotting fewer amounts of product on the graph (Q´), due to a higher price for consumers (Pd) and a lower perceived price for producers ().
Due to the effect of this tax, the balance would be as follows:
- T=Pd-Ps
- Ps=Pd-T
Practical example of the effect of the producer tax in microeconomics







