It is likely that if your child has a disorder, it will be included in neurodevelopmental disorders, since they are the ones that are They are most often diagnosed during childhood, although they can also be diagnosed in adolescence or young adulthood. adult.
If you notice that your child or yourself have difficulties or alterations in communication, many more difficulties than peers in literacy or mathematics, in making a priori uncontrollable motor movements, difficulties in concentration, impulsiveness and hyperactivity and difficulties in relating to others it is very possible that you have a disorder of neurodevelopment. In this Psychology-Online article, we will tell you what the types of neurodevelopmental disorders most common, what symptoms each of them presents and what is the best treatment in each case.
Index
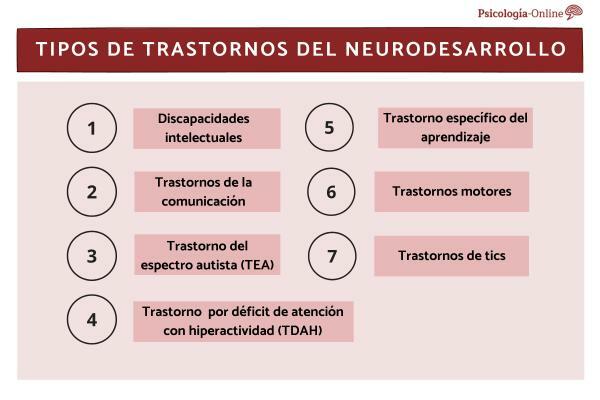
- What are developmental disorders
- intellectual disabilities
- communication disorders
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Specific learning disorder
- motor disorders
- tic disorders
What are developmental disorders.
According to the APA (American psychiatric association)[1], Developmental disorders are a group of neurologically based disorders that they start during the period of child development. They often manifest before the boy or girl starts school. As a consequence, this produces deficiencies in the school, social, academic or occupational sphere.
Intellectual disabilities.
The symptoms manifested by people with intellectual disabilities are the following:
- Deficit in reasoning.
- Difficulties in problem solving and planning.
- difficulties in Abstract thinking and conducting trials
- Difficulties in academic learning and from experiences.
- Score below an IQ of 70 on standardized intelligence tests.
- Difficulties in meeting sociocultural standards.
- Adaptive deficit that limits functioning in one or more activities of daily living: communication, social participation, and independent living.
Treatment of intellectual disabilities
The treatment of neurodevelopmental disorders varies depending on the symptoms and characteristics of each one. In this case, the first thing is to carry out secondary prevention, that is, start the intervention as soon as possible. Early detection is very important of intellectual disabilities to prevent the appearance of associated pathologies, achieve functional improvements and enable an adaptive adjustment to the person and their environment.
Specifically, in cases of intellectual disability, the intervention has two main strategies:
- Individualized planning (IP) support: the needs of the person will be evaluated and the goals and desired life experiences will be identified. Next, the individualized plan will be developed and implemented. Finally, this will be supervised and constantly evaluated in order to make the necessary modifications. In these cases, we can find from IP in schools, adapting the curriculum to the needs of the child, to external reinforcements such as re-education to improve their intellectual abilities.
- person centered planning: It is a collaborative process to help the person access the supports and services that they need to achieve a higher quality of life based on their own preferences and values with the following objectives paramount:
- Be present and participate in life in the community.
- Maintain and create bonds of satisfactory relationships.
- Express preferences and make decisions in the activities of daily life.
- Have the opportunity to develop activities with social recognition and live with dignity.
- continue developing personal skills.

Communication disorders.
There are multiple communication disorders, so their symptoms will vary depending on each specific disorder. In general, the most frequent symptoms of communication disorders are:
- Difficulties in aspects of production, mainly in motor function.
- Late appearance of language.
- Dyslalias.
- Motor alteration that involves the bucophonatory organs.
- Difficulties in the production of sound due to some anatomical alteration of the bucophonatory apparatus.
- Dysphemia or stutter.
- Impaired language comprehension.
- Massive creep inability.
- Speak hardly intelligible.
- Difficulty evoking words.
- Difficulties in communication skills.
- Difficulties in the construction of sentences or speech in general.
When carrying out the treatment of this type of neurodevelopmental disorders, you must go to a speech therapist. The objective is offer tools to the boy or girl to communicate despite their difficulties and work on the specific aspects that are altered. In addition, there are some treatments, such as the Hanen program, that teach parents how to improve their children's language skills.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
people with autism spectrum disorder present the following symptoms:
- Qualitative alterations in social interaction.
- Difficulties of emotional reciprocity.
- Qualitative alterations in communication.
- Presence of stereotyped language.
- limitation on symbolic game.
- Restricted, repetitive and stereotyped behavior patterns.
Autism Spectrum Disorder Treatment
Intervention programs for the treatment of ASD include theories based on evolutionary and developmental psychology, as well as learning and behavior modification. We highlight the following recommendations:
- Treatment should be started as soon as possible.
- Implement psychoeducational programs of a certain intensity (15-20 hours a week when the child is low-functioning).
- Train parents and/or direct caregivers.
- Set work objectives aimed at functionality, seeking to generate learning in different contexts and people.
- Give academic support.
- Work on communication difficulties.
- train the social skills.
- Promote personal autonomy.
- Reduce behavior problems with parent training.

Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Within neurodevelopmental disorders we also find attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The main symptoms of this condition are:
- Attention difficulties.
- Impulsiveness.
- hyperactivity
If you want to know more about this disorder and its symptoms in more detail, consult the following articles on ADHD in children Y ADHD in adults.
ADHD treatment
The most efficient ADHD treatment is a multimodal treatment or multidisciplinary that combines pharmacological, psychological and psychopedagogical therapy. Therefore, it is important to address the following aspects:
- Psychoeducation of the disorder and/or associated disorders or problems.
- Training for parents to manage the behavior of their children, either individually or in groups.
- Psychological intervention aimed at the boy or girl.
- Application of cognitive-behavioral techniques in playful environments.
- Training in working memory.
- School intervention, making the relevant adaptations.
- Psychopedagogical intervention treating the associated deficits, as well as strategies and techniques of study and organization and planning.
- Pharmacotherapy.
Specific learning disorder.
The characteristic symptoms of specific learning disorder are:
- Dyslexia: difficulties in reading and writing. In this article, we show you exercises to detect dyslexia.
- Dyscalculia: difficulties in mathematics.
- nonverbal learning disorder: alteration of some motor functions, difficulty in the perception and organization of visual information, problems with social interaction, lack of awareness of time, difficulties in pragmatic aspects of language and visible academic repercussion, above all, in graphics, reading, mathematics, art and education physical.
Specific learning disorder treatment
The treatment will vary substantially depending on the learning disorder that we intend to treat. Usually there is to perform accommodations at school and work with reeducations with the aim of compensating for the difficulties associated with each particular disorder and enhancing strengths. Let's see how to focus treatment according to the type of learning disorder you have:
- Dyslexia: it is important to make school adaptations and a good re-education in literacy with the aim of improving reading mechanics, although if the child is already in the last cycle of school age, the objective should be to find strategies compensatory. The re-education of writing will be aimed at not making phonological or orthographic errors. In this article you will see how to help a child with dyslexia.
- Dyscalculia: carry out re-education with the aim of reinforcing logical reasoning. Do not focus only on skills and abilities related to problem solving and mathematical operations, but that it is also necessary to work on the concept of number, series, classifications, equalization, use of work strategies and practice.
- nonverbal learning disorder: have to work the self-esteem, in addition to the capacities and abilities in which it presents greater difficulty.

Motor disorders.
Another group of very common neurodevelopmental disorders are motor disorders. The symptomatology of this type of conditions is usually the following.
- Alterations in coordination.
- Repetitive motor behaviors: hand flapping, body rocking, head banging, biting or hitting.
- Deficit in the execution and acquisition of motor skills.
- Clumsiness, slowness or inaccuracy in the execution of the movement.
The treatment of motor disorders must be carried out by a physiotherapist in coordination with other professionals that he or she sees fit.
Tic disorders.
Tic disorders are one of the most common groups of neurodevelopmental disorders in which the following symptoms are manifested:
- Presence of simple motor tics: blinking, winking, facial grimaces, movements of the nose or mouth, movements of the head, elevation of the shoulders or contractions of the extremities.
- Presence of complex motor tics: touching objects or people, stepping back, simultaneously extending arms and legs, making obscene or socially inappropriate gestures, or repeating the movement observed in another person.
- Presence of simple phonic tics: throat clearing, cough, nasal inspiration or guttural sound.
- Presence of complex phonic tics: repeat the last word or phrase pronounced by another person, repeat the same word or phrase repeatedly, verbalize obscene or socially inappropriate words, change the accent or intonation of the speech.
The best treatment for tic disorders is psychoeducation and symptom monitoring, followed by specific treatment of comorbid disorders and training in habit reversal and exposure technique and response prevention as psychological techniques. Ultimately, pharmacological treatment can be carried out and, if this also does not work, deep brain stimulation will have to be applied.

This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Types of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, we recommend that you enter our category of Clinical psychology.
References
- American psychiatric association, (2014). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM – 5. Madrid Spain. Pan American Medical Publishing.
Bibliography
- Ezpeleta, L. and Bull, J. (eds.) (2016). Developmental psychopathology. Madrid: Ed. Pyramid.