The human body has a wide variety of organs that are vital for people, each one of them has specific functions. If there is something wrong with any of these organs, this can lead to complications.
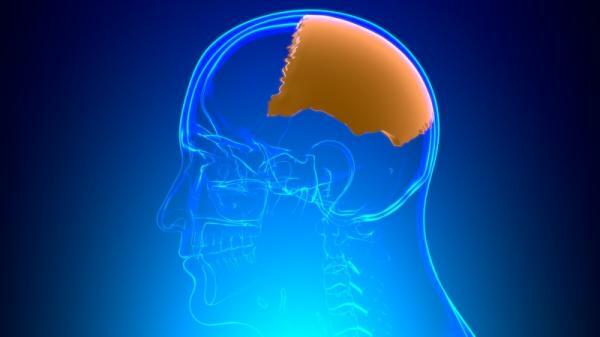
Although we know that the brain is the place where a large number of internal processes take place that allow we can develop our lives without thinking or reflecting on how this happens, the truth is that it does not happen by Magic. There is a region located in the brain that is very important for the development of the vital functions of the human being: we speak of the parietal lobe. In this Psychology-Online article, we will provide you with information about the parietal lobe: function, parts, characteristics and lesions.
Index
- What is the parietal lobe
- parietal lobe function
- Parts of the parietal lobe
- Characteristics of the parietal lobe
- parietal lobe lesions
What is the parietal lobe.
The parietal lobe is a part of the cerebral cortex
This part is located in the center of the brain and is close to the occipital lobe, the temporal lobe and the frontal lobe.
Parietal lobe function.
What does the parietal lobe do? In general, the main function of the parietal lobe is sensory data integration, which corresponds to the union of information from both inside and outside the body.
On the one hand, the neurons that allow the processing of symbolic information are located here: words, gestures, phrases, among others. This fact is related to the channels of social comunication that the human being possesses.
On the other hand, the parietal lobe is responsible for translating the data that originates in the human body. As an example, we can mention that body movements, touch or vision, among others, can be understood thanks to the work of the parietal lobe. In other words, the parietal lobe has the quality of unify the information originated in different sectors of the human body.
Parts of the parietal lobe.
The parietal lobe is divided into five parts, each with different qualities that respond to its functioning. Below we explain each of them:
- primary somatosensory cortex: is responsible for receiving data associated with the face and the opposite side of the body. In other words, the left part of the parietal lobe is connected to the information that arrives from the right sector of the right hemisphere of the body.
- Secondary somatosensory cortex: is the sector that translates electrical neural signals throughout the body.
- association area: this part studies and relates movements with images, spatial dimensions and memory.
- lower parietal: linked to the interrelation of sounds.
- intraparietal sulcus: this sector intervenes in the processes of learning.
Characteristics of the parietal lobe.
As we have already mentioned before, the parietal lobe is involved in certain complex processes that take place in the human being. In this section, we will highlight the main characteristics that emerge:
- Incidence in memory: the ability to store information can be achieved thanks to the mediation of the parietal lobe. This occurs because there are neural components that act within the hippocampus of the brain, which help make it possible to retain data.
- Emotional regulation: Mood, although it is mainly conditioned by the experiences that the person has lived, is contemplated given the intervention of the parietal lobe. In turn, the integration of sensory data is related to the way they are assimilated.
lesions in the parietal lobe.
We can delimit three types of possible lesions that can be caused in the parietal lobe. Although their severity is directly linked to the consequences produced, there are general criteria for identifying parietal lobe injuries:
- Right parietal lobe: the alterations produced here may account for difficulties in maintaining attention to stimuli located on the left side of the body. An example of this problem is contralateral negligence.
- Left parietal lobe: lesions produced in this area interfere with the performance of the right side of the body. As an example, we can mention Gerstmann syndrome given the difficulty in carrying out motor and intellectual activities.
- Both lobes: damage to the right and left lobes can lead to deficiencies in both hemispheres of the body. As a result, difficulties appear that correspond to sensitivity, touch, temporality and spatial location, among others.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Parietal lobe: function, parts, characteristics and lesions, we recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Stelzer, F., Cervigni, M. A., Martino, P. (2010). Neural bases of the development of executive functions during childhood and adolescence. A review. Chilean Journal of Neuropsychology, 5 (3), 176-184.
- Tornese, E., Mazzoglio and Nabar, M.J., Doglotti, C. g. (2015). Structural and functional correlates of the parietal lobe in females with dementia of the Alzheimer type by magnetic resonance imaging and single photon emission tomography. Argentine Magazine Anatomy, 6 (3), 128-147.
Parietal lobe: function, parts, characteristics and lesions