The brain is the most important organ in the human body. Within the medical sector, there is a large amount of research related to the different parts of the brain and their main functions. Technological advances have also allowed us to access a large number of studies on areas of the brain such as the ventricular system.
For all these reasons, today we have more information regarding this specific area of the brain, which is involved in a large number of vital processes. If you want to know about it, don't miss this Psychology-Online article about it. Cerebral ventricular system: what it is, parts and functions.
Index
- What is the cerebral ventricular system
- Parts of the cerebral ventricular system
- Functions of the cerebral ventricular system
- Alterations of the cerebral ventricular system
What is the cerebral ventricular system.
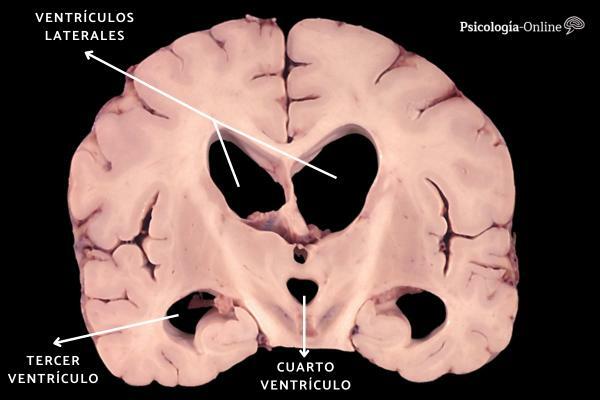
The cerebral ventricular system is a area composed of cavities called ventricles located in the brain. Specifically, it is made up of four interconnected cerebral ventricles, through channels and openings, between which the cerebrospinal fluid circulates.
This system of interconnected cavities is responsible for maintaining and protect the structure of our brain and within them the cerebrospinal fluid is formed and circulates, which is essential to preserve our body.
Parts of the cerebral ventricular system.
As we mentioned before, the cerebral ventricular system is made up of four main ventricles with different scopes. Next, we will explain the main characteristics of each of them:
- Lateral ventricles (first and second): are located within the brain hemispheres, specifically on the sides, and are connected to the temporal, parietal, occipital and frontal lobes. This area is responsible for making complex neural connections.
- third ventricle: is a flattened cavity located in the center of the cerebral hemispheres. In turn, it is connected to several regions that are part of the cerebral cortex. Among the most important are the diencephalon, the hypothalamus, the pineal gland and the thalamus, among others.
- fourth ventricle: extends from the mesencephalic aqueduct to the central canal of the upper part of the spinal cord. Given its location within the cerebral ventricular system, it maintains an important relationship with the spinal cord, responsible for the nerve connection between the brain and the various parts of the Body.
Functions of the cerebral ventricular system.
Once the anatomy of the cerebral ventricular system has been identified, it is important to know what its function is. Therefore, next, we will show you what the ventricular system of the brain does:
- Cerebrospinal fluid production: The presence of this liquid is essential to care for and protect the body. On the one hand, the cerebrospinal fluid is responsible for producing and storing nutrients, which favors the development of physical and intellectual activity. On the other hand, cerebrospinal fluid helps prevent major complications that can result from brain and spinal cord injuries.
- brain preservation: andhe cerebral ventricular system is involved in removing harmful materials that can damage the cerebral cortex. In turn, it is responsible for maintaining the internal balance of the different brain structures so that they function properly.
- Protection: taking into account the production of cerebrospinal fluid, we must add that this substance protects the body against any external pathogen. Furthermore, the cerebral ventricular system develops an immunity capacity that is consolidated over time.
- brain buoyancy: this quality marks a clear incidence in relation to the physical weight of the brain with respect to that of the organism. In other words, cerebral buoyancy makes it possible to regulate and reduce the weight of the brain.
Alterations of the cerebral ventricular system.
The alteration of the ventricular system can cause the development of different pathologies. In the following lines we will show you the main alterations of the cerebral ventricular system and its consequences.
- Alzheimer's: This degenerative condition occurs due to the death of neurons. When this happens, the spatial reduction caused by neuronal loss causes the ventricles to dilate. This demonstrates the clear relationship between memory as a vital function and the cerebral ventricular system.
- Meningitis: the irruption of pathogenic agents hinders the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- ventriculitis: This pathology is a condition of the ventricles that can cause certain organs of the body to not work properly.
- hydrocephalus: this disease consists of an injury that causes an excessive increase in the production of cerebrospinal fluid. Hydrocephalus can cause brain atrophy or metabolic disorders, among others.
- Schizophrenia: a serious mental disorder characterized by the presence of hallucinations, delusions and difficulties in establishing personal relationships. One of the main causes of schizophrenia is the spatial enlargement of the cerebral ventricles. If you want to know more about this disease, in this article you will find information about the types of schizophrenia and their characteristics.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Cerebral ventricular system: what it is, parts and functions, we recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Ordoñez-Rubiano, E.G., Baquero, P., Cifuentes-Lobelo, H., Cortés-Lozano, W., Patiño, J., Ordonez-Mora, E. (2016). Embryology of the cerebral ventricular system. Chilean Journal of Neurosurgery, 42 (1), 156-159.
- Torres-Corzo, J., Rodríguez-Della Vecchia, R., Rangel-Castilla, L. (2005). Observation of the ventricular system and subarachnoid space of the base of the skull by flexible neuroendoscopy: Normal structures. Mexico Medical Gazette Magazine, 141 (2), 165-168.


