It is often said that human beings are not coordinated, not only when relating to other people, but also in some projects that we face. Sometimes what we tell ourselves to do is not coordinated with our actions. The same could be transferred to the body, since it is possible that there is no coordination between the different parts that compose it.
On certain occasions, fatigue and daily stress produce involuntary movements that do not correspond to the thought we had had. However, there are other situations that represent important problems that we must take into consideration. In this Psychology-Online article, we will provide you with information about the types of ataxia and their characteristics.
Index
- What is ataxia and its effects
- Dominant and recessive hereditary ataxias
- Nonhereditary ataxias
What is ataxia and its effects.
What is ataxia? ataxia is a motor disorderwhich affects the coordination of the movements of different parts of the body. In general, this usually causes difficulties in the precision and speed of the person, since it can affect their way of speaking, walking or moving within a certain space.
Being a degenerative process, the effects of ataxia can arise in the short, medium and long term, depending on the characteristics of each person and the intensity of the clinical picture. Also, these types of conditions can seriously impair quality of life of people if they do not receive early treatment based on recognized clinical studies and endorsed by the scientific community.
Dominant and recessive hereditary ataxias.
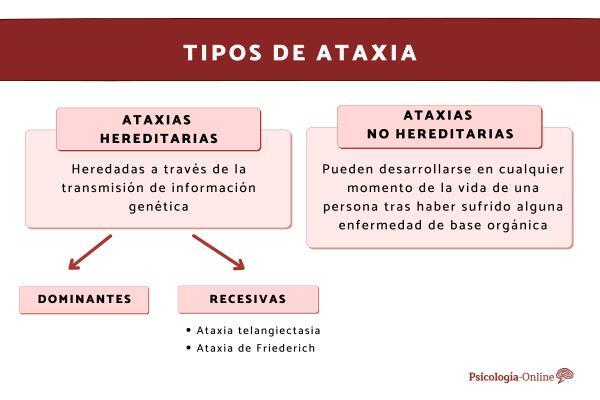
First of all, we must take into account that aSome ataxias can be inherited through the transmission of genetic information of a person's parents. In turn, this type of hereditary ataxia can be classified as dominant or recessive, depending on the nature of each of them.
Next, we explain the characteristics of dominant and recessive hereditary ataxias:
Dominant hereditary ataxias
Dominant hereditary ataxias correspond to those conditions in which Dominant genes causing ataxia predominate. In other words, in this type of hereditary ataxia, the genes that transmit the motor disorder inherited are manifested.
Recessive hereditary ataxias
Although this type of condition is also a product of Genetic heritage, the main difference with respect to the dominant hereditary ataxias is that the symptoms Often appear progressively from certain situations that act as triggers. In general, these symptoms can be detected in childhood or during certain times of adulthood.
We can distinguish two main types of recessive hereditary ataxias:
- Ataxia telangiectasia: It usually begins before the age of five and can cause loss of muscle mass, difficulties in eye and gait coordination, and immunodeficiency, among others.
- Friedrich's ataxia: also begins in childhood and symptoms may include complications in motor coordination and vision, lack of mobility in the extremities or difficulties in speech and in eating food, among others.

Nonhereditary ataxias.
This type of picture has the particularity that it can develop at any time in a person's life after having suffered some organic-based disease, or have been exposed to any stressful situation that triggers the symptoms of ataxia.
Unlike the hereditary ones, non-hereditary ataxias are not the result of genetic transmission, but can be contracted by other circumstances. In this way, there are cases in which the symptom picture does not manifest itself despite the fact that a person may be a carrier of the genes that cause the condition.
When do symptoms of ataxia appear?
How does ataxia start? Despite the characteristics described above, we must know that ataxias do not develop in the same way in all cases. Sometimes the origin of the symptoms begins in the first years of life, which can affect the motor coordination, eye movements, walking, fine and gross motor skills. On other occasions, however, the onset of these inconveniences may occur later in life and their condition may be greater or lesser in each person.
However, in all cases the diagnosis must be made by a specialized mental health professional who evaluates the clinical qualities of each patient according to aspects such as age, genetic background or pre-existing diseases, among others.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Types of ataxia and their characteristics, we recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Betancourt Fursow, Y., Jiménez León, J.C., Jiménez Betancourt, C.S. (2013). Acute ataxias in childhood. Update Journal in Child Neurology IV, 73 (1), 30-37.
- Palencia, R., Galicia, G., Alonso Ballesteros, M.J. (2004). hereditary ataxias. Journal of the Bolivian Society of Pediatrics, 44 (188), 120-127.


