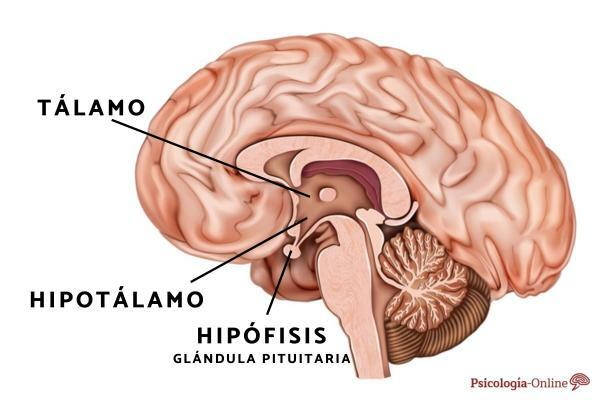
The storage of favorable information is one of the most important capacities that human beings possess. Throughout history, several researchers have been interested in understanding how memory works. In this sense, it is known that the brain is one of the vital organs that must be present in order to lead a healthy life. For this reason, it becomes essential to know that the data stored in various areas of the cerebral cortex have different entities. While there are words, scenes, experiences, sounds and memories that can be brought to the consciousness voluntarily, there are manifestations that do not depend on the intentionality of a person. In other words, one type of memory requires a concrete effort to recover information and the other has the peculiarity of being involuntary.
In this Psychology-Online article we will provide you with information about the difference between implicit and explicit memory.
Implicit memory consists of the ability to recover information from previous experiences that is done involuntarily. For this reason, it does not require a specific effort on the part of the person to make a certain situation aware. Next, we will see the main features:
- Non verbal: Implicit memory is not linked to word processing. Given this, it is about the acquisition of skills and behavioral patterns.
- involuntary learning: Due to the previous point, people who learn a skill do not need to deposit a large amount of energy to obtain favorable results.
- adaptive power: As a result of the need to carry out behaviors linked to survival in different environments, implicit memory allows a person to adapt to the environment they are in.
Types of implicit memory
In turn, this condition of the central nervous system has some particularities that define it. In the following lines you will find the main types of implicit memory:
- Procedural memory: is responsible for learning motor actions and behaviors. In effect, it allows a person to remember how to carry out a motor skill. As examples, writing, driving a car, and playing the guitar can be cited.
- Priming: consists of the acquisition of a subsequent response to an exposed stimulus. In turn, the link can be made between images and/or words. For example, a person can complete a sentence even though it is missing letters or words because his or her mental schemas have the information corresponding to the visual stimulus.
- Classical conditioning: accounts for a specific response to a specific stimulus. For example, Pavlov's investigations into a dog's responses to food had the effect of secreting saliva.
In the following article you will find information about the different Types of human memory.

Explicit memory is represented by the acquisition of data that is carried out voluntarily. In this sense, it becomes necessary for the person to dedicate time and effort to achieve the collection of information that is stored as memories. Here we will locate the characteristics of explicit memory:
- Aware: remembering events, actions and thoughts requires a personal decision to obtain the data sought.
- Influence of context: The action of time and space is crucial for data collection to be carried out effectively.
- Attention for: frequently, the attention span must be activated to reach the desired references.
Types of explicit memory
On the other hand, it is important to mention that there are two types of explicit memory:
- Episodic memory: the episodic memory lies in the storage of biographical data that occurs in a specific context. An example of this could be a memory of a vacation or an argument that occurred a few days ago.
- Semantic memory: accounts for the knowledge of concepts and historical facts that is not linked to a specific time and space. Examples of this type of memory include assimilating the countries that make up the European Union or knowing how air conditioning works.
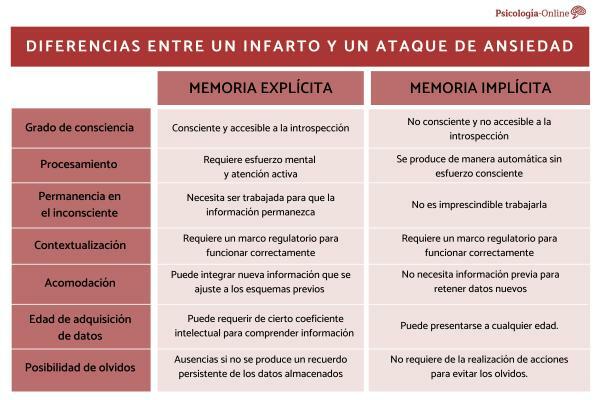
Finally, it is important to distinguish some differences between explicit and implicit memory:
- Level of consciousness: While in explicit memory it is important to make a voluntary effort, implicit memory allows the collection of unconscious data.
- Possibility of forgetting: on the one hand, explicit memory is more associated with absences if there is no persistent memory of the stored data. On the other hand, implicit memory does not require taking actions to avoid forgetting.
- Permanence in the unconscious: Explicit memory needs to be worked on so that the information remains. However, this is not essential in implicit memory.
- Contextualization: Explicit memory requires a regulatory framework to function correctly, but implicit memory can be developed without it.
- Accommodation: Explicit memory can contemplate new information that fits the previous schemas of the knowledge, while implicit memory does not need to have a prior framework to retain data novel.
- Data acquisition age: Explicit memory may require a certain IQ to understand elaborate information, so, in most cases, age can be a determining factor. On the contrary, implicit memory allows a human being to learn at any age.
On the other hand, in this article we explain the Difference between episodic and semantic memory.

This article is merely informative, at Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.