The neurotransmitters They are the chemicals that are responsible for the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next through synapses. We define neurotransmitters then, as those molecules that send chemical and electrical information. neurotransmitters determine human behavior, the perception of our senses and even regulate the emotions.
Do you want to know what neurotransmitters are, how many types are there and which is the relationship between neurotransmitters and emotions? Then we recommend you continue reading this interesting article on Psychology-Online.
Index
- What are neurotransmitters?
- Types of neurotransmitters that regulate emotions
- Acetylcholine
- Norepinephrine
- Dopamine
- GABA and Glutamate
- Serotonin
- Endorphin
What are neurotransmitters?
We define neurotransmitters as Chemical components that are found in our brain and are responsible for transmitting specific information from one neuron to another. Each neurotransmitter has a different chemical composition that allows them to perform
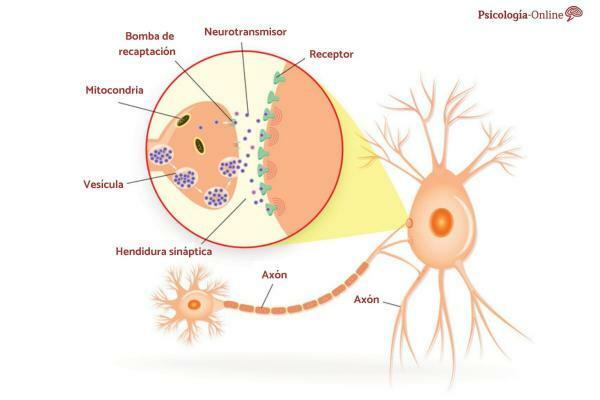
These substances are located inside the neuronal cells until the moment in which the synapse occurs. At that moment, they travel from one neuron to another to transmit one information or another.
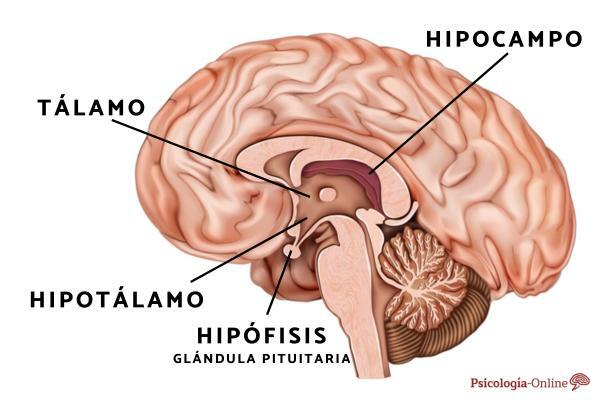
In addition to brain neurons, neurotransmitters are also found at the axon terminal of motor neurons, where they stimulate muscle fibers to contract. They and their close relatives are produced in some glands such as the pituitary and adrenal glands.
What is the synapse?
Neurons communicate with each other through their branches (axon). To carry out this communicative act, they use a series of electrical and chemical discharges that drive neurotransmitters to travel through the synaptic space to reach the other cell neuronal.
We must bear in mind that in our nervous system, we have billions of neuronsThese cells form a large network of neuronal tissue with which we receive and transmit information throughout our body.
Can you imagine the complexity of our nervous system? Now that you know what neurotransmitters are, we are going to tell you how they are related to emotions.

Types of neurotransmitters that regulate emotions.
As we indicated at the beginning of this article, neurotransmitters are capable of regulating our emotions. Although it seems incredible, sadness, joy and even feelings such as nostalgia or the state of infatuation They are born from the interaction of the different neurotransmitters in our brain. Each molecule in its proper measure is capable of producing and regulating one emotion or another.
Among the main types of neurotransmitters that regulate emotions, we highlight the following:
- Acetylcholine
- Dopamine
- Norepinephrine
- Gaba
- Glutamate
- Serotonin
- Endorphin
Next, we are going to describe in a detailed way what these neurotransmitters are and how they work.
Acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter to be discovered. It was isolated in 1921 by a German biologist named Otto Loewi.[1], who subsequently won the Nobel Prize for his work. Acetylcholine has many functions:
- It is responsible for much of the muscle stimulation, including the muscles of the gastro-intestinal system.
- It is also found in sensory neurons and the autonomic nervous system, and is involved in REM sleep programming.
The famous botulinum poison works by blocking acetylcholine, causing paralysis. The derivative of botulin called botox is used by many people to temporarily eliminate wrinkles - a sad chronicle of our time, I would say. On a more serious note, there is a link between acetylcholine and Alzheimer's disease - there is a loss of about 90% of acetylcholine in the brains of people suffering from this disease debilitating.

Norepinephrine.
In 1946[2], another German biologist whose name was Von Euler, discovered norepinephrine (formerly called norepinephrine).
Functions of norepyrephrine
Norepinephrine is strongly associated with putting our nervous system on "high alert." It is prevalent in the sympathetic nervous system, and increases heart rate and blood pressure. Our adrenal glands release it into the bloodstream, along with its relative epinephrine. It is also important for memory formation. Stress tends to deplete our adrenaline store, while exercise tends to increase it. Amphetamines ("speed") work by causing the release of norepinephrine.
Dopamine
Another relative of norepinephrine and epinephrine is dopamine . It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means that when it finds its way to its receptors, it blocks that neuron's tendency to fire. Dopamine is strongly associated with reward mechanisms in the brain. Drugs like cocaine, opium, heroin, and alcohol promote the release of dopamine, just like nicotine does!
The serious mental illness called schizophrenia has been shown to involve excessive amounts of dopamine in the frontal lobes, and drugs that block dopamine are used to help schizophrenics. On the other hand, too little dopamine in the motor areas of the brain is responsible for Parkinson's disease, which involves uncontrollable body tremors.
GABA and Glutamate.
Next, we are going to define two very interesting types of neurotransmitters: GABA and Gluatamate. Both have very similar functions, however, one is inhibitory and the other excitatory.
GABA
In 1950, Eugene Roberts and J. Awapara discovered GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid), another type of inhibitory neurotransmitter. GABA acts as a brake on the excitatory neurotransmitters that lead to anxiety. People with little GABA tend to suffer from anxiety disorders, and medications like Valium work by increasing the effects of GABA. If GABA is absent in some parts of the brain, epilepsy occurs.
Glutamate
Glutamate is an excitatory relative of GABA. It is the most common neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, and it is especially important in relation to memory. Interestingly, glutamate is actually toxic to neurons, and too much of it would kill them. Sometimes brain damage or a stroke can lead to too much damage and end up with many more brain cells dying than the trauma itself. ALS, more commonly known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is caused by excess glutamate production.
Serotonin
Serotonin has been found to be intimately related to emotion and mood. Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, anger management problems, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. Too little also leads to an increased appetite for carbohydrates (foods rich in starch) and sleep problems, which are also associated with depression and other problems emotional
Prozac and other medications help people with depression by preventing neurons from taking in excess serotonin, so there is more floating around the synapses. Interestingly, a little warm milk before bed also increases serotonin levels. As mom may have told you, she helps you sleep. Serotonin is a derived from tryptophan, found in milk. Heat is just for comfort!
On the other hand, serotonin also plays a role in perception. Hallucinogens like LSD work by binding to serotonin receptors in the perceptual pathways. If you want to know more about this molecule, we show you the following article about what is serotonin and what is it for.
Endorphin.
Finally, to finish this article on the relationship between neurotransmitters and emotions, we will talk about endorphin.
In 1973, Solomon Snyder and Candace Pert of John's Hopkins discovered endorphin[3]. Endorphin is the short name for "endogenous morphine" (present in heroin). It is structurally very similar to opioids (opium, morphine, heroin, etc.) and has similar functions: it is involved in the reduction of pain and pleasure, and opiate drugs work by binding to endorphin receptors.
It is also the neurotransmitter that helps bears and other animals hibernate. Consider this: Heroin slows your heart rate, respiration, and overall metabolism - exactly what you would need to hibernate. Of course, heroin sometimes totally slows down: Permanent hibernation.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to The relationship between neurotransmitters and emotions, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.
References
- espeimenti di Lowei, G. Dimostrazione della neurotrasmissione.
- Von Euler, U. S. (1956). Noradrenaline.
- Simantov, R., Kuhar, M. J., Uhl, G. R., & Snyder, S. H. (1977). Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 74(5), 2167-2171.