Currently in psychology, there are many theories that aim to increase our emotional well-being as well as our own motivation for us to carry out our vital goals and to experience the benefits that our own development brings personal. One of these theories is that of the human motivation of the psychologist Abraham Maslow who identified what are the main needs of human beings and classified them into categories according to a hierarchical order of importance to survival and our own ability to motivation.
This humanistic psychologist suggests that every time people are satisfying our own needs, they go more appearing along the way, which we are also going to try to satisfy in order to feel fuller and made. In this Psychology-Online article, we will delve into the Maslow's theory of human motivation. In addition, we are going to explain you with a good summary and examples what this theory consists of.
For the psychologist Abraham Maslow, the needs that human beings have impel us to have the willpower to overcome all the difficulties that come our way every day. When we talk about motivation, we mean that desire that drives us to want to achieve some goal and satisfy our human needs. This is why Maslow dedicated himself to investigating what are the needs that people have and finally created a model known as
- Basic or physiological needs: refers to the basic needs for the survival of the person.
- Security: refers to the need to feel safe and protected in life.
- Membership: It is the need that people have to belong to a social group and feel accepted by it.
- Recognition: They are all those needs for recognition and acceptance of oneself and on the part of others.
- Self realisation: This is the highest level in the hierarchy of needs and to reach it, we need to have all other needs satisfied as it refers to the feeling of being happy in life.
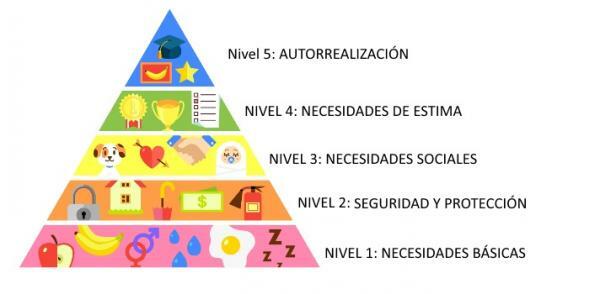
Next, we will show you each of the Maslow's pyramid needs with their respective examples to finish better understanding what each of them refers to.
1. Basic or physiological needs
As basic needs are those involved in our own survival, there is the power breathe, eat and drink, dress, have sex, etc. For example, a person who has adequate clothing to cover himself from the cold in winter and can feed on adequately, it can be said that the basic or physiological needs are covered that allow survive.
On the contrary, a person who lives on the street and is hungry and cold, has no covers these kinds of needs that we need to survive so we run the risk of not being able to achieve it.
2. Security
Within this group of needs are all those that provide us with security and that make us feel protected by providing us with independence and self-sufficiency. For example, a person who has a roof to sleep on, is healthy enough to work and able to pay the rent of an apartment and be a manager, a person who has this type of coverage is considered need.
On the contrary, a person who does not have this type of need well satisfied may don't have a job, do not have good health and do not have a roof where to sleep that provides security and comfort, among other things that make the person not have their own independence.
3. Membership
A person who has this type of need covered feels part of a social group and therefore feels appreciated and valued by the members of that group. For example, a person who has a family that he knows he can count on, a group of friends to go to when he needs company and some advice, he may have a partner he can trust and intimacy sexual.
On the contrary, a person who does not have that need satisfied, she feels alone and isolated from society since she does not belong to any social group nor does she have a family to support her.
4. Recognition
When a person has more or less satisfied all the needs described above, this is the next need that he will want to satisfy. A person who has this need satisfied feels self-confident and knows how to recognize his personal worth. A clear example would be a person who performs effectively in his work, likes what he does and other people recognize him for his work.
On the contrary, a person who does not have this need covered, has low self-esteem, does not consider himself suitable for what he does, does not feel comfortable in her work and no one recognizes his work.
5. Self realisation
A person who is at this level is because he has the other needs fully satisfied. An example of a person at this level is independent, has confidence in herself, is considered a successful person and she feels that she has everything she needs to be happy. Likes help others and have an open mindShe respects the ideas and opinions of others as well as her own, she likes to be constantly learning new things and is very concerned about her personal development.
The opposite of this person would be the one who despite being successful and who likes what they do, does not feel completely satisfied and has the permanent feeling that something is missing to achieve happiness.

One of the most recent and curious applications of the theory of human motivation is Maslow's pyramid in economics. Today, human impulses to buy and consume products according to their needs are studied.
In marketing, motivation is applied to campaigns for the sale of products and services. In this way, companies modify the advertising message of what they want to sell in relation to the need they think they can satisfy.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.


