How does our ability to communicate and understand language work?
This question has been studied from various branches of psychology and has been a mystery until the arrival of scientific and technological advances to this discipline. Neuroimaging and neuropsychology techniques have confirmed the existence of two fundamental areas for speech and language understanding: Broca's area and Wernicke's area. Both systems were discovered centuries ago, but it was not until a few decades ago that it was found out exactly how they work.
In this article from Psychology-Online "Broca and Wernicke's area: differences and functions"We will talk about these very important sets of neurons in our brain, where they are found and how exactly they work.
Index
- Where the Broca and Wernicke area are located
- Broca and Wernicke's area: differences
- Wernicke's area: functions and diseases
- Broca's area: functions and diseases
Where the Broca and Wernicke area are located.
First of all, it is important to be clear that these areas are part of the Central Nervous System (CNS), that is, they are located in the lobes of the brain.
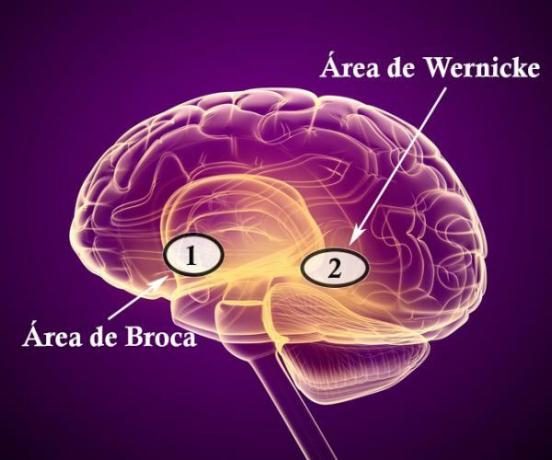
- Broca's area (1) is in charge of producing language and is found in the left hemisphere, more specifically in the lower part of the frontal lobe.
- Wernicke's area (2) is responsible for sound comprehension and can usually be found in the left hemisphereAlthough 30% of left-handed people and 10% of right-handed people are in the right hemisphere. This area belongs to temporal lobe and is highly related to the auditory zone.
- The broca's area and Wernicke's area are connected by a group of nerve fibers known as the Aqueado fascicle.
Here is a picture to show where Broca and Wernicke's area are located
Broca and Wernicke's area: differences.
Although both systems are closely related to the ability to communicate of the human being, there are several differences between the Broca and Wernicke area that we must to mention.
First of all, it is important to know that the area of Drill is involved in the ordering of phonemes (minimum unit of language) in words and in the union of words to form sentences and sentences, while Wernicke's area is responsible for processing the sounds we hear and relating them to speech and language we already know.
That is, thanks to the area of Wernicke we understand what we are told[1]. In addition, Wernicke's area is next to the system in charge of processing sounds, so it is easier to remember its function if we remember where it is.
In summary: the main difference between the Broca area and the Wernicke area is that the former is responsible for plan the way we speak and the second takes care that let's understand what we are told.
Here is an image of the connection between Broca's area and Wernicke through the arcuate fascicle:
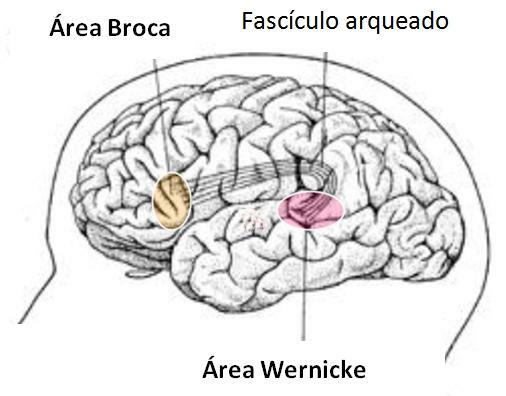
Image: PsicoWisdom
Wernicke's area: functions and diseases.
Finally, to understand the Broca and Wernicke's area: differences and functions, it is essential to know the origin of both terms.
These concepts were discovered from medical cases in which people who suffered injuries in certain areas of the brain could not either speak or understand language and, upon doing a forensic analysis, they discovered that all the injured areas were the themselves.
In 1874, Karl Wernicke discovered that certain patients whose brains had been damaged could not speak in a structured way. Although they pronounced well and their words made sense, the message could not be understood. What happened to them then, is that they were unable to understand language.
The lesion that all these patients had in common was located in the posterior part of the temporal lobe, in Brodmann areas 21 and 22[2]. From the study of this type of lesions, Wernicke named the affected area after him, stating that it was in charge of understanding language.
Today, we define Wernicke's area as a set of neural networks in charge of processing the typical sounds of speech and expressing them as words and concepts, that is, their function is to decode phonemes. Despite not being a "word selector" system, this area is necessary to carry out the production of a fluent and understandable speech.
Wernicke's aphasia
By affecting the decoding of phonemes, Wernicke's aphasia is characterized by inability to understand a message or repeat it. As we have commented previously, patients with this type of injury do not correctly understand what they are told and, as a result of this, they do not generate a logical discourse.

Broca's area: functions and diseases.
This area of the cerebral cortex was discovered before the Wernicke Area, 13 years earlier to be more specific. In 1861, the neurosurgeon Paul Broca discovered that some people with speech difficulties had a lesion in Brodmann's areas 44 and 45[2]. Today, we know that Broca's area is part of a neuron system in charge of ordering phonemes (minimum units of language) into words and, furthermore, it is also an access area for verbs and functional words.
That is, Broca's area is the one in charge of the relational aspects of language and grammar. and, in addition, it is the area of the nervous system in charge of storing functional words such as verbs.
In summary, the main functions of Broca's area are:
- Produce logical and understandable sounds (He speaks)
- Process language
- Control the neurons in charge of facial movement
Broca's aphasia
People who suffer an injury in this area end up presenting Broca's aphasia, this disease neurophysiological is characterized by the difficulty in producing words and joining elements in a sentence (loss of communicative ability). That is, a person with Broca's aphasia will not be able to express himself correctly or form complete sentences.
These types of injuries are quite disabling but can be improved through rehabilitation and lots of practice to re-educate the facial muscles.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Broca and Wernicke's area: differences and functions, we recommend that you enter our category of Neuropsychology.
References
- Castaño, J. (2003). Neurobiological bases of language and its alterations. Rev Neurol, 36(8), 781-5.
- Brodmann, K. (1909). Comparative location of the cerebral cortex. On Comparative location of the cerebral cortex. Brodmann's areas are a very widespread classification system of the cerebral cortex in the world of neuroanatomy.
Bibliography
- Binder, J. R. (2015). The Wernicke area Modern evidence and a reinterpretation. Neurology, 10-1212.


