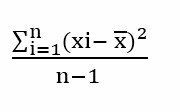It is known as Bayes theorem, to the preposition compiled from the memoirs of the mathematician and priest of English origin Thomas Bayer. Who, two years after his death in 1761, expresses probability (the measure of certainty linked to a event) conditional on a random event given some information in advance about the event.
In other words, said theorem calculates the probability "A" conditioned by the information "B". Achieving the determination of the probability of the causes from the effects that have been observed.
Advertisements
In this article you will find:
Mathematical expression of Bayes' theorem
It is known as an evidentiary probability that evaluates the probability of a hypothesis, specifying some a priori possibility, then updated in the light of new data.
Bayes provided a set of standard formulas and procedures to perform this calculation.
Advertisements
In this mathematical operation 3 classes of probabilities intervene, which are the following:
- P (Ai) or a priori probability of an event “A”.
- P (Ai/ B) or a posteriori probability of an event “A”, (when information is obtained that an event B has occurred).
- P (B / Ai) or likelihoods of event “B” are assumptions that would occur at each event Ai.
Mathematically, Bayes' theorem is equal to the quotient of the product of probability “B” given (Ai), P (B / Ai) (where B is the known event and “Ai”The events conditioned) by the probability P (Ai) between the sum of each probability that contains the known event for each known event.
Advertisements
In short, the numerator is the conditional probability and the denominator is the total probability.

Advertisements
Bayes problem weaknesses
Statesmen have questioned the theorem based on the limitations of its application, since it is valid only when disjoint and exhaustive events are fulfilled.
Similarly, specialists in traditional statistics confirm that only statistics based on repeatable and empirically testable experiments, because Bayesian statistical probabilities admit conditions relative.
Advertisements
Applications of Bayes' Theorem
Bayes' theorem is used to calculate the possibilities of an event that is given or not by another previous event, which allows evaluating in what way subjective probabilities are transformed, the more new information is possessed of a done.
In addition to being applicable to models based on subjective knowledge and empirical evidence. It also applies to models that are used, for example, in merging data from a system.
Likewise, it is considered an excellent model or method to evaluate new information and review previous estimates based on limited data. to know then if they are in one state or another, if it is applied in an ideal way then the data collection is made effective to take better decisions.
Conditions for applying Bayes' theorem
- The events “Ai”Must be mutually exclusive, that is, only one of them can happen.
- The union of its possibilities is the total, that is, the unit, that is, it must be a complete system. And each one must be different from zero.
- A case "B" of which all the probabilities are known is established.
- All the conditional probabilities P (B / Ai).
Advantages of applying Bayes' theorem in everyday life
- It can be approached in such a way that benefits are obtained in some fields.
- Continuous analysis of the information is possible, although if the variability between data is high, some method is necessary to reach reliable solutions.
- Meta-Analysis: seek to accumulate varied information to arrive at an exact appreciation of a problem
- Evaluation of small-scale studies with the information of others, because the development of these on a global scale it is not always possible, and at the sample level it does not have total veracity, the Bayesian approach allows to ratify and refute.
- Decision studies.
Importance of Bayes' Theorem
In the statistical field, Bayes' theorem allowed the resolution of multiple probability problems, its importance lies in its application, since it is fundamental in any science, since it allows to demonstrate the intrinsic relationship with the understanding of the probabilities of the events caused once the effects have been established facts.
Bayesian probability makes it possible to convert a subjective probability into a real one when it is modified based on new information.
The empirical evidence that according to the statisticians acts as a basis for the application of this theorem has specific applications in the different branches of the Medicine, from the diagnosis of cancer to the prevention of diabetes, also has less sophisticated uses such as evaluating the possibilities in a game of decks.
Recapitulating, this theorem serves to evaluate events a priori and a posteriori, taking into account facts that may or may not be subjective and based on the possibilities that these events trigger, obtain data that as knowledge will allow or not establish a plan of action.