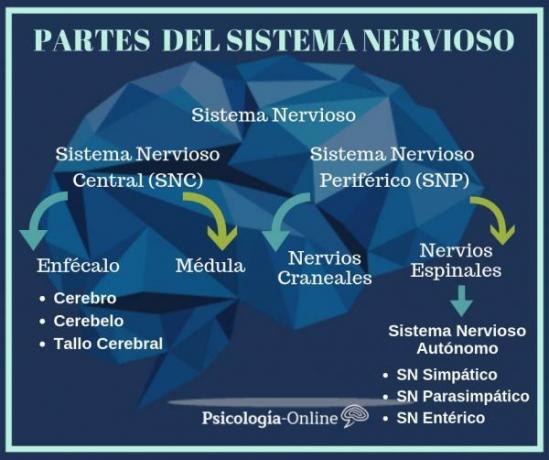
The cerebrum is the largest portion of the brain, where the cerebellum and brainstem are also located. Specifically, the brain is made up of two hemispheres, the right and the left, and, in turn, is also divided into different lobes made up of cortical and subcortical structures. One of the best known is the amygdala, due to its involvement in the processing of emotions, and others less well known, such as the habenula.
If you are interested in knowing more about this small structure, do not miss the explanation that we offer you in this Psychology-Online article. We'll talk about the habenula: what it is, parts, function and location, as well as what their inputs and outputs are and their implications for human behavior.
Index
- What is habenula
- Habenula function
- Location of the habenula
What is habenula.
The habenula, or habenular nucleus, is a fairly unknown structure or, if not more, one that is unfamiliar, even to professionals in the area. Specifically, it is a
Inputs and outputs involving the habenula
On the one hand, the habenula participates in the afferents through the stria medullaris thalami, the anterior perforated substance, the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, limbic regions, and the caudate nucleus.
On the other hand, the efferents in which the habenula participates are the intrapeduncular nucleus, in the dorsal and medial nuclei of the raphe, in the dorsal nucleus of the tegmentum and in the superior colliculus, also related to structures that release dopamine, noepinephrine and serotonin.
Parts of the habenula
Mainly, in the habenular or habenula nuclei we can distinguish the following Two parts:
- The lateral habenular nucleus.
- The medial habenular nucleus.
function of the habenula.
Despite being a fairly unknown structure for many, the main function of the habenula is modulate various brain structures. In addition, it is closely related, taking into account the neurotransmitters that it modulates, with pleasure, gratification, positive reinforcement and cognition.
Processes linked to the habenula
Habenular nuclei have been related to the following processes:
- Sleep-wake.
- The reward response because of its relationship with the limbic system.
- The sexual behavior.
- The behavioral response of pain.
- decision making: makes us take risks in situations where we can express fear.
- Evokes emotions from smells, since it has olfactory afferents.
Effects of alterations in the habenula
Alterations and dysfunctions of the habenula have revealed the following symptoms:
- hyperarousal in those who suffer from major depression.
- Tendency to show less interest and pleasure in ordinarily pleasant things.
- excessive focus in negative aspects.
- Symptoms or signs similar to those suffered by people with attention deficit disorder and hyperactivity.
Implication of the habenula in the consumption of nicotine
Notably, some important implications for nicotine use have been discovered.
It appears that the medial habenula-interpeduncular nucleus circuit protects animals (and presumably also our species) from consuming large amounts of nicotine. Neurons in the medial habenula, midbrain region, contain a special type of nicotinic cholinergic receptor that includes an alpha 5 subunit. Neurons expressing these receptors send their axons to the interpeduncular nucleus, located in the midline of the midbrain, caudal to the medial habenula. This pathway appears to be part of a system that inhibits the reinforcing effects of nicotine. Fowler et al. (2011) found that deletion of the gene responsible for the alpha5 cholinergic receptor synthesis increased high-dose nicotine self-administration. They also found that the technique reduced nicotine's ability to activate the nucleus interpeduncular, and that the interruption of the activity of this nucleus increased the self-administration of nicotine.

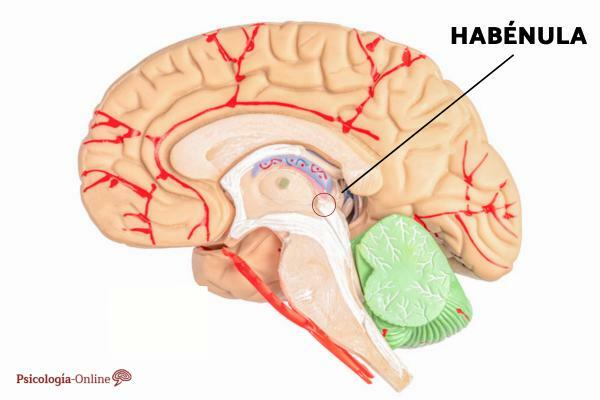
Location of the habenula.
the habenula is located in the epithalamus, that is, inside the diencephalon. Specifically, it is located in the forebrain next to structures such as the thalamus, the hypothalamus and the pineal gland. These structures that stand out for their connection with the limbic system.
It should be noted that the habenula, or habenular nuclei, is connected to the pineal gland and facilitates the connection between the limbic system and the reticular formation.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Habenula: what it is, parts, function and location, we recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Carlson, N. R. (2014). physiology of behavior. Madrid. Pearson Education, S.A.
- Fakhoury M, Dominguez-Lopez S. (2014). The role of habenula in motivation and reward. Advances in Neuroscience.
- Lawson RP, Nord CL, Seymour B, Thomas DL, Dayan P, Silling S, Roiser JP., (2017) Disruptes habenula function in major depression. Molecular Psychiatry. 22(1) 202-208.
- Lee Y, Goto Y., (2013). Habenula and ADHD: convergence on time. Neuroscience behavioral review. 37 (8) 1801-1809.
Habenula: what it is, parts, function and location