It is not always easy to describe whether what we feel is fear or anxiety. In reality, the emotion of fear is a symptom present in the clinical picture of anxiety, so being so similar it is normal to confuse them. In addition, it is usually perceived eventually in a different intensity gradation.
Both indicate the perception of danger and prepare our body to give an alarm response. In this sense, what varies is the intensity of the perceived danger and, consequently, the intensity of our reaction. In this Psychology-Online article, we will talk in depth about what is the difference between anxiety and fear.
Index
- what is anxiety
- what is fear
- How to differentiate fear and anxiety
What is anxiety.
anxiety is a emotional state associated with a condition of alertness and fear, generally excessive compared to the real danger. Even so, it is not an abnormal phenomenon, since it is a basic emotion that implies a state of activation of the organism when the subject perceives that he is facing a dangerous situation.
So what are anxiety symptoms? An immediate tendency to explore the environment for explanations and escape routes, as well as a series of physiological phenomena such as increased respiratory and heart rate, sweating or vertigo, among others.
When the activation of the organism becomes excessive, this can produce an anxiety disorder that can affect and complicate the life of the person who suffers from it. In this article you will see what are the types of anxiety and their symptoms.
symptoms of anxiety
The anxious clinical picture manifests itself in many ways. Let’s see what are the main symptoms of anxiety:
- Nervousness.
- Apprehension.
- Insomnia.
- Apnea.
- Easy to cry.
- Palpitations.
- Soft spot.
- Cramps in the stomach.
In general, it is common for all people to have anxiety at some point in their lives, due to the overstimulation to which we are exposed. Even so, if they are properly motivated, anxiety becomes a transient sensation. On the contrary, episodes of anxiety that arise without a real justification are the origin of excessive reactions that characterize the anxiety disorders.

What is fear.
The term fear refers to a emotion that arises in the presence of unexpected or imminent danger. Even so, it can also indicate an imaginary concern, apparently not linked to a real danger situation.
It should be noted that fear is one of the primal emotions and it has an adaptive function that protects the individual against danger or threat (real or imagined). From the first years of life, it performs fundamental evolutionary functions and without this mechanism we would be continually putting our safety at risk.
symptoms of fear
How does fear manifest? Here are its main symptoms:
- increased heart rate: Allows the person to react faster. The heart increases its activity to increase blood flow and quickly deliver sugar and oxygen to the body.
- increased breathing: the tense muscles of the body hinder the expansion of the lungs. The rhythm of breathing changes.
- Tingling, feeling of numbness and hot flashes: the increase in blood pressure is perceived, mainly, in the extremities. This activation produces reddening of the skin and heat to which the body responds by cooling itself through sweat.
- Muscular stiffness: all muscles tend to stiffen. They are tense because they are ready to jump if necessary.
- Goosebumps: the contraction of the muscles also affects the tissues of the skin.
- Obfuscation, narrowing of the visual field and dizziness: Increased pressure may cause a feeling of dizziness. The pupils of the eyes dilate to help focus.
- Digestive disorders, nausea and abdominal disorders: digestion is interrupted and the corresponding energies are used to activate the organism against danger.
- Confusion and daze: the focus of attention is placed on the danger and any other thought is dissociated. You can perceive a strangeness of oneself.

How to differentiate fear and anxiety.
Anxiety and fear, although they have a very strong link, are not the same. Let us see the main differences between fear and anxiety.
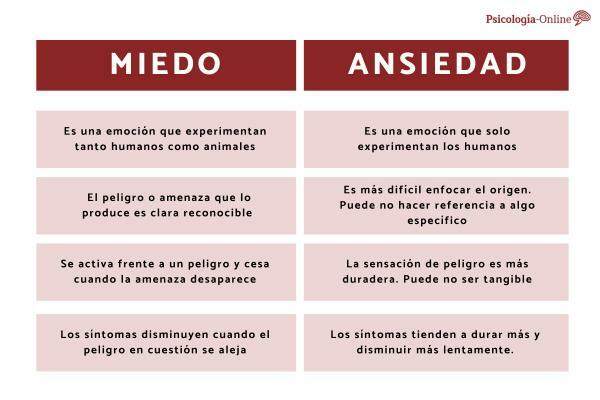
1. who experiences it
Do all living things experience fear and anxiety? Let's see it:
- Fear is a state animals also feel and experience, especially mammals.
- anxiety is an emotion typically human, evolved from fear, parallel to the progression of our cognitive capacities of imagination, anticipation and design.
2. Way
The way we perceive fear and anxiety is different. We show it below:
- When we are afraid, the threat or danger we encounter is clear and well defined in our eyes, that is, the object of our fear is well focused.
- When we experience anxiety it is much more difficult to focus on the origin and object of our experiences. In fact, anxiety can be described as a state of open concern, for example, in a certain area of our lives, without referring to something specific and determined.
3. Duration
Although the sensation experienced is similar, its duration is different. Let's see the difference between anxiety and fear in terms of duration:
- Fear is activated in the face of real danger and, once cease the threat, disappear.
- Anxiety can be activated in the face of real danger, but also in the face of a perceived threat, that is, non-tangible and shared, often vague and poorly defined. The sense of danger lasts longer due to the difficulty of identifying the causes.
When it comes to differentiating this aspect, for example, many of us experience fear when we are near a cliff, but we know that not everyone is afraid of getting on the crowded tram at night. morning.
4. Symptom perception
As for how they manifest, both fear and anxiety are accompanied by physiological symptoms, but their duration is different. Let's see when they manifest and disappear:
- symptoms of fear tend to decrease when the stimulus in question moves away and we no longer feel threatened by it.
- In the case of anxiety, the subjective experience and its physiological modifications tend to last longer and decrease more slowly. People often describe being in a state of general tension. An "alert feeling" as if something negative is going to happen at any moment.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Difference Between Anxiety and Fear, we recommend that you enter our category of Clinical psychology.
Bibliography
- Andre, C. (2006). Psicologia Del Miedo/The Psychology of the Fear: Fears, Anguish and Phobias/Fright, Anguish and Phobias. Editorial Kairos.
- Sierra, J.C., Ortega, V., Zubeidat, I. (2003). Anxiety, anguish and stress: three concepts to differentiate. Magazine Dis-estar E Subjectivity, 3 (1), 10-59.


