Our mind processes two types of thinking known as convergent and divergent thinking. The first refers to the logical and analytical part and, on the other hand, the second manages the creative and imaginative part.
Both are fundamental to our ability to understand, two sides of the same coin, two ways of thinking completely opposite to each other and yet extremely important in the conduct of our lives everyday. In this Psychology-Online article, we will see together the differences between convergent and divergent thinking.
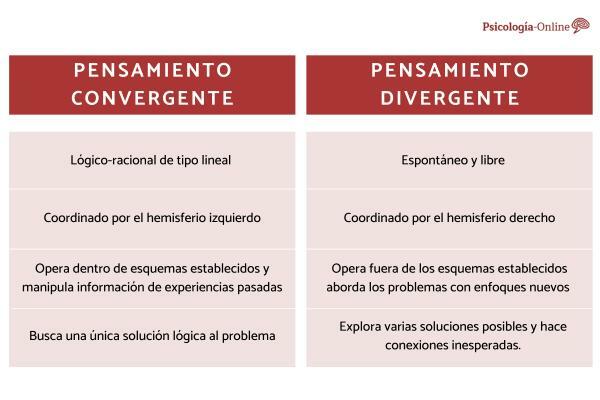
Convergent thinking refers to reasoning logical, rational, deductive and focused. Its purpose is to produce the best possible answer to a problem, with little or no ambiguity. Next, we show you what are the characteristics of convergent thinking:
- Values speed, accuracy and logic.
- focuses on recognize what is familiar, reapply techniques and accumulate information.
- It is more effective in situations in which an already existing response can be found, elaborating it on the basis of decision making.
- The solution derived from convergent thinking is the best possible answer, in general terms and in most specific cases.
- It is related to knowledge because it involves manipulation of information or past experiences using standard procedures. Knowledge can be an important aspect of creativity, as a source of ideas, suggests possible pathways and provides criteria for evaluating the effectiveness and originality of solutions.
When convergent thinking is used to solve a problem, it is often judged by conscious reference to data and probability criteria. Let's look at a typical example of convergent thinking:
The logical solution to the problem of the continuation of a numerical series, for example, 1, 3, 4, 8... 32? It is about identifying the criterion that operates in the sequence and, therefore, the missing number that meets the sequence (16). There is a criterion and a possible solution, so the operations of thought must converge towards its identification.
divergent thinking is spontaneous and free. It underlies the purest forms of creativity and in many ways represents true creativity. Discover the traits that characterize divergent thinking:
- generate ideas exploring many possible solutions, often in parallel.
- Ideas can emerge in a casual cognitive fashion, in the form of epiphanies or flashes of genius ("a-ha!" moments).
- are explored several possible solutions and unexpected connections are made.
- The traits that favor this way of thinking are nonconformity, curiosity, willingness to take risks, courage, perseverance and resilience.
divergent thinking operates on open problems and with multiple solutions. Let's look at an example:
If the answer to the question about "what is the use of a cap" is that it serves as a headdress and that is all, the thought that operates is convergent, since it unites the object with its obvious and common function. On the other hand, if it is answered that it is used to ask for alms, to collect pebbles or to use it as a shooting target, the thought that intervenes is of a divergent type.
If you want to know more, do not miss this article about the divergent thinking: what it is, characteristics and examples.

The development of creativity it often involves both convergent and divergent thinking. Neither one is better or worse than the other, but rather everyone has their own qualities. In all fields, such as art, science, or business, the most creative solutions often involve multiple sources of both modes of thought.
Joy Paul Guilford was one of the first authors to systematically study creativity and the first to distinguish between convergent and divergent thinking. He discovers below what their differences are and how they complement each other:
- convergent thinking: logical-rational linear type and is coordinated by the left hemisphere. It operates within established schemes and therefore approaches the problem with a certain method, finding the only possible solution with that method, which is then a conventional solution. Accumulate the knowledge, experience and ideas necessary to activate the unconscious work of divergent work.
- Divergent thinking: it is coordinated by the right hemisphere, seat of creativity, free associations and image reasoning. It operates outside of established schemes and, therefore, tackles problems with new approaches and arrives at original solutions.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.