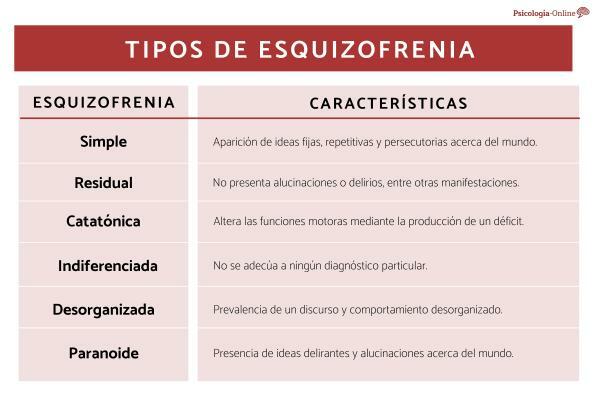
There are 6 types of schizophrenia, each with particular characteristics: simple schizophrenia, residual schizophrenia, catatonic schizophrenia, undifferentiated schizophrenia, disorganized schizophrenia, and paranoid schizophrenia. Schizophrenia is one of the most well-known pathologies today due to the complexities it raises. Beyond any definition we have about it, it is important to keep in mind that there are various types of this mental disorder, each of them with some characteristic feature that distinguishes it from the rest. Each schizophrenia has specific symptoms, causes, and treatments.
In this Psychology-Online article we will provide you with information about the 6 types of schizophrenia and their characteristics.
Index
- simple schizophrenia
- residual schizophrenia
- catatonic schizophrenia
- Undifferentiated schizophrenia
- disorganized schizophrenia
- Paranoid schizophrenia
Plain schizophrenia.
Simple schizophrenia is a subtype of mental disorder characterized by
- Duration of one year or more.
- Hallucinations.
- delusions.
- disorganized language.
- Apathy.
- Abulia.
- Lack of attention and concentration.
In this article we explain what is the Difference Between Delusion and Hallucination.
Causes of simple schizophrenia
Beyond understanding the main symptoms, it is interesting to think about the origins that give rise to the manifestations of this type of pathology. Here we will locate the most relevant causes:
- Genetic factors: all those neuronal alterations originate through genetic transmission. In this sense, heredity plays a fundamental role in understanding the vicissitudes of each person.
- Environmental factors: the traumas experienced during childhood can be the initial kick for the development of simple schizophrenia. Unpleasant experiences in a person's life correspond to situations in which it has not been possible to defend oneself from insults or mistreatment, among others.
To treat simple schizophrenia it is necessary to carry out a psychological treatment that allows ordering the coordinates of the patient's life through the relevant tools. Similarly, the supply of antipsychotic medication helps regulate the incidence of delusions and hallucinations that occur.
residual schizophrenia.
Unlike the previously described subtype, residual schizophrenia no hallucinations or delusions, among other manifestations. For this reason, it is considered a milder type of schizophrenia. Here are the most frequent symptoms:
- Duration of one year or more.
- motor inhibition.
- Abulia.
- Lack of verbal and non-verbal communication.
Causes of residual schizophrenia
Beyond this type of presentation, it is necessary to distinguish what may be the causes that originate the picture. Here we will describe them:
- Environmental factors: like simple schizophrenia, one should not leave aside the experiences of a person that determine their personality. Within the most common situations, it is possible to distinguish excessive levels of anxiety and/or stress against which there is a lack of resources.
- Genetic factors: In the event that a relative has been diagnosed with residual schizophrenia, there is a high chance that the person will develop the same clinical manifestations.
In general terms, it is essential to evaluate each particular case to define which is the best treatment for each person. In these cases it is often necessary to resort to psychiatric medication to decrease the intensity of the picture in conjunction with antidepressant drugs and anxiolytics. Likewise, it is essential to establish a specialized follow-up with a psychologist to monitor the patient's life and be able to establish order.

catatonic schizophrenia.
Catatonic schizophrenia shares some symptoms with other types of schizophrenia, however, one of its differential characteristics is that alters motor functions by producing a visible and noticeable deficit.
To correctly define the clinical picture, it is necessary to locate some of its most common symptoms:
- Hallucinations.
- delusions.
- Unbelievable behaviors.
- Lack of motor activity.
- Mutism.
- Repetitive movements.
- Imitation of another person's movements.
- Imitation of other people's speech.
Causes of catatonic schizophrenia
The origins give certain explanations to the physical, emotional and behavioral manifestations of each human being. In these lines, we will point out the causes:
- Genetic factors: Some investigations have confirmed that the biological factor could be one of the causes of this disorder. In this sense, in the majority of investigations it has been verified that there are genetic disorders that are transmitted from generation to generation, a fact that can impair the neuronal functioning of each person and, consequently, affect the motor area.
- Environmental factors: Certain stressful situations and events in the person's life may also have contributed to the worsening of the condition.
Despite these difficulties, it should be mentioned that there are treatments that help improve the quality of life of those who suffer from catatonic schizophrenia. In general terms, psychiatric medication is an indispensable requirement to control the possible crises that manifest in this mental disorder. In turn, a psychological treatment is usually important to set life goals and establish a social bond.
Undifferentiated schizophrenia.
As its name indicates, undifferentiated schizophrenia is characterized by the presence of various symptoms typical of mental illness, but does not fit any particular diagnosis. For this reason, it is necessary to make a distinction with respect to the other types of schizophrenia.
Here are some of its most characteristic symptoms:
- Hallucinations.
- Social isolation.
- Abulia.
- stiff body movements.
- Lack of spoken language.
- disorganized behavior.
Causes of undifferentiated schizophrenia
Through the detection of these indicators, it is possible to arrive at an adequate diagnosis. Beyond everything, it is convenient to provide certain precisions about the reasons that cause undifferentiated schizophrenia. In the following points, we will address this topic:
- cerebral accidents: alteration of neuronal functioning due to blows, bruises, cerebrovascular accidents, among others.
- Consumption of drugs: the intake of toxic substances is another factor that can harm the person who has undifferentiated schizophrenia. In this sense, there are stronger drugs that cause serious damage to the Central Nervous System.
- Environmental factors: living conditions are a fundamental core to take into account for these people. At a general level, these are situations of physical, verbal violence, abuse, among others.
Although it is true that undifferentiated schizophrenia is one of the most complex conditions within the mental disorders, we currently have certain variables to achieve a partial or total remission of the symptoms. Due to the gravity of the frame, the supply of several antipsychotic medications is usually necessary and establish a lifelong psychological treatment. It should be noted that both spaces should be in contact to unify criteria and avoid confusion in the patient.
disorganized schizophrenia.
It corresponds to a subtype of schizophrenia that stands out for the prevalence of disorganized speech and behavior. As with other types of schizophrenia, disorganized schizophrenia has several symptoms in common with other subtypes of this disorder.
The most characteristic symptoms of disorganized schizophrenia are:
- incoherent language.
- strange behaviours.
- emotional instability.
- Lack of social contact.
- Apathy.
- Abulia.
- delusions
- Hallucinations.
Causes of disorganized schizophrenia
As previously described, it is necessary to understand the origins of each mental illness. In the case of disorganized schizophrenia, we will locate the most relevant causes:
- genetic factorss: despite the fact that it is not completely proven, it is estimated that the presence of mental disorders such as depression or psychosis constitute an increase in the development of this type of schizophrenia. In this sense, it is known that alterations in neuronal connections respond to the way external stimuli are processed.
- environmental factorss: here it is possible to locate consumption of toxic substances, unpleasant life experiences, among others. However, this will depend on each particular case.
Regarding the appropriate type of treatment, the general recommendation is based on the administration of antipsychotic medication to regulate the functioning of the central nervous system. However, this should be reinforced by a adapted psychological treatment to the needs of each patient to set life goals.

Paranoid schizophrenia.
Finally, paranoid schizophrenia is characterized by the presence of delusions and hallucinations about the world, a distinctive feature that may be absent in other types of schizophrenia.
Next, we show you the most common symptoms of this type of schizophrenia:
- hallucinations.
- delusions of persecution.
- Altered perception of reality.
- Lack of affectivity.
- Certainty.
Causes of paranoid schizophrenia
In general, the causes of schizophrenia are not fully determined. However, some investigations have yielded accurate data about the origins:
- Genetic factors: genetic inheritance is closely linked to the development of the disease. If either parent was diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia, there is a good chance that the person will repeat the same pattern.
- Environmental factors: the way of raising and the interpretation of the facts appears as a clear indicator of this pathology. During a person's lifetime, they may have seen or heard loved ones act in certain ways. If you have a distorted idea of reality, it may happen that you imitate these behaviors.
Although these difficulties present serious damage to social and family life, paranoid schizophrenia can be addressed through a pharmacological treatment based on antipsychotic drugs that are supplied by a health professional mental. In tune with this process, the person should undergo psychological therapy to put together life strategies in the face of complexities that they could go through.

This article is merely informative, at Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Types of schizophrenia and their characteristics, we recommend that you enter our category of Clinical psychology.
Bibliography
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th edition). Arlington: Panamerican Medical Editorial.
- López Rodríguez, P., Sanmillán Brooks, H. E., Cainet Beltrán, A. R., Olivares Martinez, O. (2015). Some theoretical considerations related to the study of schizophrenia. Scientific Information Magazine, 93 (5), 1189-1206.


