Image: Universia
There are many models in psychology designed to seek our well-being and guide our internal motivation. One of the best known models is that of Abraham Maslow, this humanistic psychologist devoted much of his career to creating a model of hierarchies of needs known as Maslow's pyramid. This model is widely known throughout the world since it is very useful in psychological practice. The main objective of the pyramid is to order our needs and establish a hierarchy.
If you are interested in Abraham Maslow's pyramid of human needs, in this Psychology-Online article, we will see Maslow's pyramid with practical examples of needs and images. We'll look at personal examples of all of Maslow's needs and even how the pyramid applies to marketing.
Index
- Contributions of Abraham Maslow
- What is Maslow's pyramid
- Examples of Maslow's pyramid
- What is Maslow's pyramid for?
- Criticisms of Maslow's pyramid model
- Maslow's pyramid in marketing
Contributions of Abraham Maslow.
Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) was an American psychologist born in Palo Alto, California. He is known for founding, along with other experts, humanistic psychology, a discipline born as an alternative to behaviorism and psychoanalysis.
Maslow was the older brother of seven children, he himself claimed that he grew up lonely, with few friends and among many books. He began his studies in psychology investigating sexual behaviors in primates, years later and after much evolution in his postulates, he brought to light a theory about human motivation called "the hierarchy of needs". One of his main mentors was Alfred Adler, a pioneer of individual psychology and a leading student of personality theories.
What humanistic psychologistMaslow explored people's internal motivations, innate desires, and the meaning of our lives. The humanistic approach focuses on developing people's potential and the qualities that distinguish us as empathic, rational and, as the name suggests, human. It is necessary to understand the theories and techniques of humanism to understand Maslow's pyramid theory exactly.

What is Maslow's pyramid.
For the psychologist Abraham Maslow, motivation is defined as the human being's impulse to satisfy his needs, these needs needed a classification or hierarchy, since some are more important for human survival than others.
In this context, Maslow proposed a theory of motivation in which he asserted that there was a hierarchy in human needs and that, in the first place, those that are considered most basic had to be satisfied. With each need covered, the human being advances in the hierarchy until the highest desires of him are satisfied.
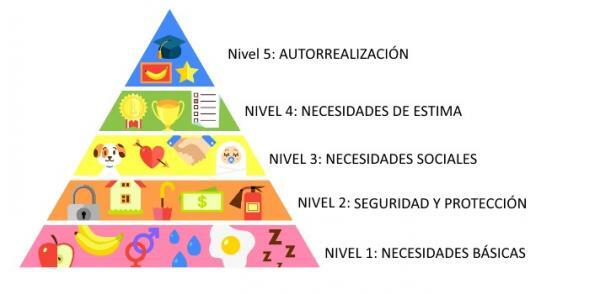
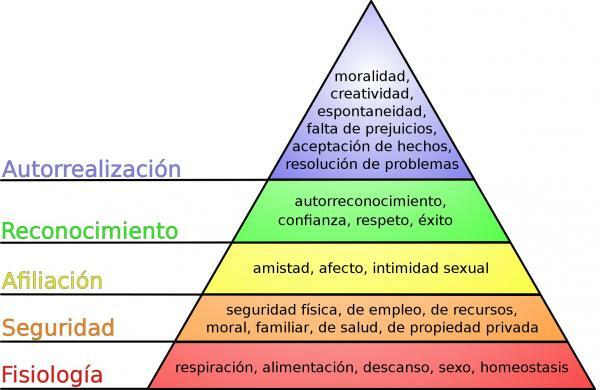
Being a hierarchical organization, this model is shaped like a pyramid and consists of five levels:
- Physiology
- Safety
- Membership
- Recognition
- Self realisation
Broadly speaking, we can affirm that the most basic needs (also known as primary needs) constitute the lowest part of the pyramid while, on the other hand, the highest or growth needs are located at the upper end of the figure. This order is because, first, Maslow says that we must take care of the needs that keep us alive, such as eating, drinking and maintaining good health. When we are stable and maintain a basic balance, we can try to meet and satisfy our needs for knowledge and personal fulfillment.
Examples of Maslow's pyramid.
Next, we will explain each level of this model and we will put practical examples to better understand how the hierarchy of human needs works. Let's look at some examples of each level of Maslow's pyramid:
1. Physiological needs
The base of this pyramid comprises the needs of our organic system. The human body must maintain a certain balance in order to function properly and this balance is achieved with proper nutrition, rest, hydration... Maslow also adds sex as a physiological necessity. Despite being a debatable element at the individual level, it is true that sex is essential for the survival of the species.
- Examples of physiological needs: the first thing we will need as a human being is to breathe, eat, drink and sleep. Until these needs are covered, we will not be able to focus on other concerns.
2. Need for security
Once basic physiological needs are met, we begin to worry about our safety. This level comprises the stability work, having a home, having resources available... feeling safe and stable reduces our alert systems and allows us to advance in the hierarchy. This level also includes needs related to the stability of the family circle.
- Example of security need: a security need is to know that we have a roof to sleep under, after having our organic state controlled, we will want to cover this type of need.
3. Need for filiation
The need for affiliation corresponds to that related to the social relationships, participation in events and meetings and acceptance of equals. The human being is social by nature (to a lesser or greater degree) and we need to maintain a circle of social networks to obtain a correct mental stability.
- Example of affiliation need: once we have a plate on the table and a roof to sleep under, we begin to worry about our friends and our peer group. Companionship, affection between other people and sexual intimacy are clear examples of this level, Maslow's pyramid.
4. Need for recognition
When we speak of recognition we refer to the need to esteem and appreciation, both for others and for the promotion of self-esteem. Inferiority complexes are born when this level of the pyramid is not satisfied.
- Example of need for recognition: For the human being, it is practically essential that someone appreciates us and values our actions. Also, strengthen the bases of self-esteem it is essential to achieve a correct mental balance.
5. Need for self-realization
According to Maslow, this last level is no longer considered a primary need. This is because we can only focus our attention on the self-actualization needs when we can fully satisfy other human needs. This level comprises emotional goals such as morality, creativity, acceptance of facts ...
- Example of the need for self-realization: When we finally feel at ease physically and mentally, we are able to direct our efforts toward higher goals. The personal and human development is completed reaching this level. An example of a person who has reached this end of the pyramid is one who has all his needs covered and dedicates much of his time to altruism, social work and growth spiritual.
What is Maslow's pyramid for?
Once we know the practical examples of each level of the pyramid, it is important to analyze the basic rules that maintain order in this hierarchy of needs:
- The behavior of human beings is altered when some of the needs are not satisfied, especially if they are basic needs.
- Physiological needs are born of the individual himself, the rest appear over time
- Non-primary needs (such as self-fulfillment) can also be satisfied even though basic needs are not fully covered. However, according to the same hierarchy of needs, it is more important to seek the satisfaction of basic needs.
- Human needs are shared by all individuals to a lesser or greater extent.
Therefore, Maslow's pyramid allows a better understanding of people's behavior.
Criticism of Maslow's pyramid model.
Although this theory still applies today, Maslow's hierarchy of priorities has some bugs at the time of analyzing how the human being acts in real life. There are cases of people who, for example, put their basic physiological needs at risk in search of self-esteem and social acceptance.
This is the case of eating disorders, people who suffer from it stop eating and come to atrophy the organic system with a goal quite far from the bases of the pyramid. Another example is infidelity behaviors in marriages, where one of the parties puts family security at risk due to other needs for self-esteem and acceptance.
Currently, the hierarchy of needs model it is not dogmatic, we know that it has flaws and that it does not always apply. Still, it is a very useful theory to learn to prioritize our lives and detect our emotional motivations.
Maslow's pyramid in marketing.
In addition to being a very widespread theory in the field of social psychology and psychotherapies motivational factors, the hierarchy of needs also applies to the economic model, more specifically in marketing. Advertising campaigns use strategies that appeal to the satisfaction of one or more needs. How can Maslow's pyramid be applied in the workplace and company? How to apply Maslow's pyramid in a product?
Let's take a look at Maslow's needs applied to cologne advertising marketing with examples, despite the fact that the product sold is a fragrance spray, the sales strategies focus the content of the ads on the affiliation and self-fulfillment needs (attractive actors and actresses, surrounded by people and many metaphors appealing to success).
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Maslow's pyramid: practical examples of needs, we recommend that you enter our category of Emotions.
Bibliography
- Castellanos, J. C. C. (2016). Neuromarketing and its relationship with the hierarchy of needs by Abraham Maslow. Contributions to the Economy, (2016-01).
- Muñoz, M. D. P. V., & de la Fuente, F. V. (2010). The Pyramid of Needs by Abraham Maslow. Negotiation strategies and tactics, 1-4.
- Maslow, A. (1951). Hierarchy of Human Needs. Mexico, FCE


