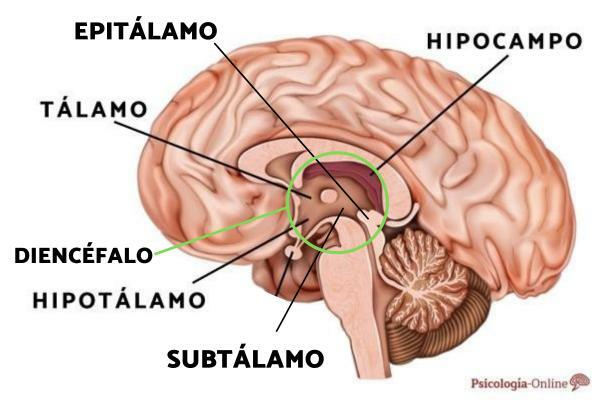
The human brain is the main organ of the nervous system, which allows the performance of the functions and processes characteristic of human beings. But do we really know what our brain is like? If the answer is no, do not hesitate to gather information about what it is like, what its parts are and its main functions.
Since information is power, the more knowledge we have, the freer we will be. For this reason, in this Online Psychology article, we bring you information about one of the most unknown brain areas. Specifically, we offer you information on the epithalamus: what it is, parts and functions.
Index
- what is the epithalamus
- Parts of the epithalamus
- functions of the epithalamus
- Consequences of lesions in the epithalamus
What is the epithalamus.
The epithalamus is a small pinkish-grey structure, specifically about 7 millimeters in length. Said structure is part of the brain or organ that controls the functions of the human being, and is located above the dorsal surface of the thalamus,
This small structure is related to the limbic system, considered the emotional brain, as it regulates human emotions and instincts. Despite its small size, the epithalamus allows the performance of essential tasks for the human being.
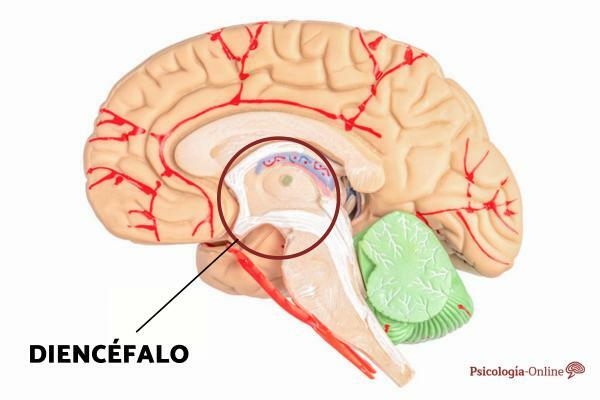
Furthermore, along with the thalamus Y the hypothalamus, forms the diencephalon or part of the nervous system that encompasses several functional areas of the human brain. You can learn more about this structure in our post Diencephalon: what it is, parts and functions.
Parts of the epithalamus.
The epithalamus is composed of two structures, mainly, of great relevance for the human being and its functioning. Both structures are detailed below:
1. epiphysis or pineal gland
This gland is located in the posterior part of the third ventricle. The pineal gland is characterized by containing glial cells, cells of the nervous system that do not have axons. Now, despite being the smallest gland in the human body, it carries out numerous processes:
- secretes melatonin from serotonin.
- Regulates the rhythms of sleep and wakefulness.
- Participate in the synthesis of endorphins and sex hormones.
- Promotes growth and sexual maturation.
- Regulates the endocrine system.
If you want to know more about this structure that makes up the epithalamus, we recommend you consult our post Pineal gland: functions, diseases and their symptoms.
2. habenular nuclei
Don't you know what the Habenula is? This structure of the epithalamus is connected to the pineal gland, and serves as a bridge to other parts of the brain. The habenular nuclei are divided into two differentiated areas:
- The lateral habenular nucleus.
- The medial habenular nucleus.
It has been proven that this structure is related to fear and the Depression. Therefore, the stimulation of this brain structure allows to improve the state of people suffering from depression. Also, it has been shown that these nuclei participate in the evocation of emotions through smells determined.
Functions of the epithalamus.
Now that you know what structures make up the epithalamus and what it regulates, it will be easier for you to understand that the functions it carried out by the epithalamus are due to the communication between the parts that compose it and its link with the system limbic
That is to say, its functionality is given thanks to the existing neuronal connections in the human brain. The functions performed by the epithalamus are related to human adaptation and survival. Among the main functions of this brain structure, the following stand out.
- Manage circadian rhythms.
- regulate energy saving.
- releases melatonin from serotonin.
- Contributes to growth and sexual maturation.
- Relate certain smells with specific emotions.
- Regulates sleep and wake cycles.
- Modulates the mood.
- Influences motivation management
- Regulates emotional processes.
- Participates in the regulation of physiological responses.
- modulate the instincts.

Consequences of lesions in the epithalamus.
The alteration or damage of any of the structures that make up the epithalamus can lead the human being to suffer from the following problems:
- Difficulty controlling instincts.
- Emotional imbalance.
- Limitation of sexual and maturational growth.
- Sleep disorder.
- Mood disturbance.
- energetic lack of control.
- Inability to evoke emotions through smells.
- Difficulty in the release of melatonin.
- Inability to regulate physiological responses.
- Appearance of psychological disorderssuch as anxiety or depression.
- Biological alteration of regular intervals of time.
This article is merely informative, in Psychology-Online we do not have the power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Epithalamus: what it is, parts and functions, we recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.
Bibliography
- Akagi, K., & Powell, E. w. (1968). Differential projections of habenular nuclei. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 132(2), 263-273. Available in: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cne.901320204
- llIll, L. s. (1985). Neurology of the hypothalamus and diencephalon Neurology of the hypothalamus and diencephalon. Arch. Invest. Med.(Mex.), 16(Suppl 3), 33. Available in: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Bruno-Estanol/publication/19318508_Neurology_of_neuroendocrinological_disturbances/links/5771e0e108ae6219474a5ee7/Neurology-of-neuroendocrinological-disturbances.pdf
- Nieuwenhuys, R., Voogd, J., van Huijzen, C., & Papa, M. (2010). Diencephalon: introduction to the epithalamus. In The central nervous system (pp. 247-251). Springer, Milan. Available in: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-88-470-1140-3_7
- Roa, I., & del Sol, M. (2014). Pineal gland morphology: review of the literature. International Journal of Morphology, 32(2), 515-521. Available in: https://scielo.conicyt.cl/scielo.php? pid=S0717-95022014000200023&script=sci_arttext&tlng=p


